Circadian clock-specific roles for the light response protein WHITE COLLAR-2
- PMID: 11283242
- PMCID: PMC86893
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2619-2628.2001
Circadian clock-specific roles for the light response protein WHITE COLLAR-2
Abstract
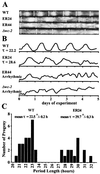
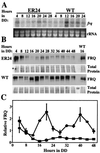
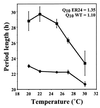
To understand the role of white collar-2 in the Neurospora circadian clock, we examined alleles of wc-2 thought to encode partially functional proteins. We found that wc-2 allele ER24 contained a conservative mutation in the zinc finger. This mutation results in reduced levels of circadian rhythm-critical clock gene products, frq mRNA and FRQ protein, and in a lengthened period of the circadian clock. In addition, this mutation altered a second canonical property of the clock, temperature compensation: as temperature increased, period length decreased substantially. This temperature compensation defect correlated with a temperature-dependent increase in overall FRQ protein levels, with the relative increase being greater in wc-2 (ER24) than in wild type, while overall frq mRNA levels were largely unaltered by temperature. We suggest that this temperature-dependent increase in FRQ levels partially rescues the lowered levels of FRQ resulting from the wc-2 (ER24) defect, yielding a shorter period at higher temperatures. Thus, normal activity of the essential clock component WC-2, a positive regulator of frq, is critical for establishing period length and temperature compensation in this circadian system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interconnected feedback loops in the Neurospora circadian system.Science. 2000 Jul 7;289(5476):107-10. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5476.107. Science. 2000. PMID: 10884222
-
Regulation of the Neurospora circadian clock by an RNA helicase.Genes Dev. 2005 Jan 15;19(2):234-41. doi: 10.1101/gad.1266805. Epub 2004 Dec 29. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15625191 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian clock genes frequency and white collar-1 are not essential for entrainment to temperature cycles in Neurospora crassa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 21;103(12):4469-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510404103. Epub 2006 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537415 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular workings of the Neurospora biological clock.Novartis Found Symp. 2003;253:184-98; discussion 102-9, 198-202, 281-4. Novartis Found Symp. 2003. PMID: 14712922 Review.
-
The neurospora circadian system.J Biol Rhythms. 2004 Oct;19(5):414-24. doi: 10.1177/0748730404269116. J Biol Rhythms. 2004. PMID: 15534321 Review.
Cited by
-
WC-2 mediates WC-1-FRQ interaction within the PAS protein-linked circadian feedback loop of Neurospora.EMBO J. 2001 Jan 15;20(1-2):109-17. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.1.109. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11226161 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors in light and circadian clock signaling networks revealed by genomewide mapping of direct targets for neurospora white collar complex.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Oct;9(10):1549-56. doi: 10.1128/EC.00154-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20675579 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythms in Neurospora crassa: clock mutant effects in the absence of a frq-based oscillator.Genetics. 2007 Mar;175(3):1175-83. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.068270. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17237512 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive modelling of the Neurospora circadian clock and its temperature compensation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(3):e1002437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002437. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22496627 Free PMC article.
-
The PAS/LOV protein VIVID supports a rapidly dampened daytime oscillator that facilitates entrainment of the Neurospora circadian clock.Genes Dev. 2005 Nov 1;19(21):2593-605. doi: 10.1101/gad.349305. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16264193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allada R, White N E, So W V, Hall J C, Rosbash M. A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell. 1998;93:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Aronson B D, Johnson K A, Loros J J, Dunlap J C. Negative feedback defining a circadian clock: autoregulation of the clock gene frequency. Science. 1994;263:1578–1584. - PubMed
-
- Aronson B D, Lindgren K M, Dunlap J C, Loros J J. An efficient method of gene disruption in Neurospora crassa. Mol Gen Genet. 1994;242:490–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
