Sustained signaling by phospholipase C-gamma mediates nerve growth factor-triggered gene expression
- PMID: 11283249
- PMCID: PMC86900
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2695-2705.2001
Sustained signaling by phospholipase C-gamma mediates nerve growth factor-triggered gene expression
Abstract
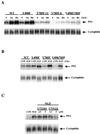
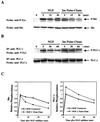
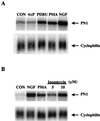
In contrast to conventional signaling by growth factors that requires their continual presence, a 1-min pulse of nerve growth factor (NGF) is sufficient to induce electrical excitability in PC12 cells due to induction of the peripheral nerve type 1 (PN1) sodium channel gene. We have investigated the mechanism for this triggered signaling pathway by NGF in PC12 cells. Mutation of TrkA at key autophosphorylation sites indicates an essential role for the phospholipase C-gamma (PLC-gamma) binding site, but not the Shc binding site, for NGF-triggered induction of PN1. In concordance with results with Trk mutants, drug-mediated inhibition of PLC-gamma activity also blocks PN1 induction by NGF. Examination of the kinetics of TrkA autophosphorylation indicates that triggered signaling does not result from sustained activation and autophosphorylation of the TrkA receptor kinase, whose phosphorylation state declines rapidly after NGF removal. Rather, TrkA triggers an unexpectedly prolonged phosphorylation and activation of PLC-gamma signaling that is sustained for up to 2 h. Prevention of the elevation of intracellular Ca2+ levels using BAPTA-AM results in a block of PN1 induction by NGF. Sustained signaling by PLC-gamma provides a means for differential neuronal gene induction after transient exposure to NGF.
Figures






References
-
- Altar C A, DiStefano P S. Neurotrophin trafficking by anterograde transport. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:433–437. - PubMed
-
- Barbacid M. Neurotrophic factors and their receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Berg M M, Sternberg D W, Parada L F, Chao M V. K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Bonni A, Ginty D D, Dudek H, Greenberg M E. Serine 133-phosphorylated CREB induces transcription via a cooperative mechanism that may confer specificity to neurotrophin signals. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1995;6:168–183. - PubMed
-
- Bourne H R, Sanders D A, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990;348:125–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
