Cyclin A is a mediator of p120E4F-dependent cell cycle arrest in G1
- PMID: 11283272
- PMCID: PMC86923
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2956-2966.2001
Cyclin A is a mediator of p120E4F-dependent cell cycle arrest in G1
Abstract
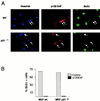
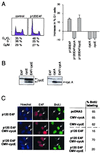
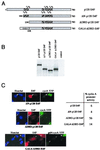
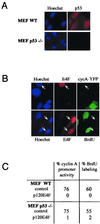
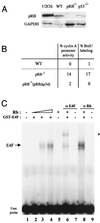
E4F is a ubiquitously expressed GLI-Krüppel-related transcription factor which has been identified for its capacity to regulate transcription of the adenovirus E4 gene in response to E1A. However, cellular genes regulated by E4F are still unknown. Some of these genes are likely to be involved in cell cycle progression since ectopic p120E4F expression induces cell cycle arrest in G1. Although p21WAF1 stabilization was proposed to mediate E4F-dependent cell cycle arrest, we found that p120E4F can induce a G1 block in p21(-/-) cells, suggesting that other proteins are essential for the p120E4F-dependent block in G1. We show here that cyclin A promoter activity can be repressed by p120E4F and that this repression correlates with p120E4F binding to the cyclic AMP-responsive element site of the cyclin A promoter. In addition, enforced expression of cyclin A releases p120E4F-arrested cells from the G1 block. These data identify the cyclin A gene as a cellular target for p120E4F and suggest a mechanism for p120E4F-dependent cell cycle regulation.
Figures





References
-
- Barlat I, Fesquet D, Brechot C, Henglein B, Dupuy d'Angeac A, Vie A, Blanchard J M. Loss of the G1-S control of cyclin A expression during tumoral progression of Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1993;4:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Barlat I, Henglein B, Plet A, Lamb N, Fernandez A, McKenzie F, Pouyssegur J, Vie A, Blanchard J M. TGF-beta 1 and cAMP attenuate cyclin A gene transcription via a cAMP responsive element through independent pathways. Oncogene. 1995;11:1309–1318. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon J I, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon G J. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Chin J W, Kohler J J, Schneider T L, Schepartz A. Protein escorts to the transcription ball. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R929–R932. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
