A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome
- PMID: 11283351
- PMCID: PMC31875
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.061034498
A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome
Abstract
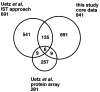
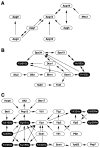
Protein-protein interactions play crucial roles in the execution of various biological functions. Accordingly, their comprehensive description would contribute considerably to the functional interpretation of fully sequenced genomes, which are flooded with novel genes of unpredictable functions. We previously developed a system to examine two-hybrid interactions in all possible combinations between the approximately 6,000 proteins of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Here we have completed the comprehensive analysis using this system to identify 4,549 two-hybrid interactions among 3,278 proteins. Unexpectedly, these data do not largely overlap with those obtained by the other project [Uetz, P., et al. (2000) Nature (London) 403, 623-627] and hence have substantially expanded our knowledge on the protein interaction space or interactome of the yeast. Cumulative connection of these binary interactions generates a single huge network linking the vast majority of the proteins. Bioinformatics-aided selection of biologically relevant interactions highlights various intriguing subnetworks. They include, for instance, the one that had successfully foreseen the involvement of a novel protein in spindle pole body function as well as the one that may uncover a hitherto unidentified multiprotein complex potentially participating in the process of vesicular transport. Our data would thus significantly expand and improve the protein interaction map for the exploration of genome functions that eventually leads to thorough understanding of the cell as a molecular system.
Figures
Comment in
-
Networking proteins in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 10;98(8):4277-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091096398. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11296274 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Blattner F R, Plunkett G, 3rd, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D, Rode C K, Mayhew G F, et al. Science. 1997;277:1453–1474. - PubMed
-
- Goffeau A, Barrell B G, Bussey H, Davis R W, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel J D, Jacq C, Johnston M, et al. Science. 1996;274:563–567. - PubMed
-
- Winzeler E A, Shoemaker D D, Astromoff A, Liang H, Anderson K, Andre B, Bangham R, Benito R, Boeke J D, Bussey H, et al. Science. 1999;285:901–906. - PubMed
-
- Ogasawara N. Res Microbiol. 2000;151:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Fraser A G, Kamath R S, Zipperien P, Martinez-Campos M, Sohrmann M, Ahringer J. Nature (London) 2000;408:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

