A novel mechanism of PKA anchoring revealed by solution structures of anchoring complexes
- PMID: 11285229
- PMCID: PMC145475
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1651
A novel mechanism of PKA anchoring revealed by solution structures of anchoring complexes
Abstract
The specificity of intracellular signaling events is controlled, in part, by compartmentalization of protein kinases and phosphatases. The subcellular localization of these enzymes is often maintained by protein- protein interactions. A prototypic example is the compartmentalization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) through its association with A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). A docking and dimerization domain (D/D) located within the first 45 residues of each regulatory (R) subunit protomer forms a high affinity binding site for its anchoring partner. We now report the structures of two D/D-AKAP peptide complexes obtained by solution NMR methods, one with Ht31(493-515) and the other with AKAP79(392-413). We present the first direct structural data demonstrating the helical nature of the peptides. The structures reveal conserved hydrophobic interaction surfaces on the helical AKAP peptides and the PKA R subunit, which are responsible for mediating the high affinity association in the complexes. In a departure from the dimer-dimer interactions seen in other X-type four-helix bundle dimeric proteins, our structures reveal a novel hydrophobic groove that accommodates one AKAP per RIIalpha D/D.
Figures



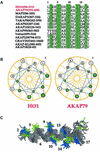

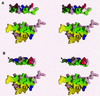
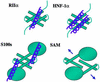
Similar articles
-
Analysis of A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) interaction with protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits: PKA isoform specificity in AKAP binding.J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 28;298(2):329-39. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3662. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764601
-
Molecular basis of AKAP specificity for PKA regulatory subunits.Mol Cell. 2006 Nov 3;24(3):383-95. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.09.006. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17081989
-
The molecular basis for protein kinase A anchoring revealed by solution NMR.Nat Struct Biol. 1999 Mar;6(3):222-7. doi: 10.1038/6663. Nat Struct Biol. 1999. PMID: 10074940
-
Anchoring and scaffold proteins for kinases and phosphatases.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:409-29; discussion 429-30. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997. PMID: 9238861 Review.
-
Mechanisms of protein kinase A anchoring.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;283:235-330. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)83005-9. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20801421 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual specificity A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) contain an additional binding region that enhances targeting of protein kinase A type I.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 28;283(48):33708-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804807200. Epub 2008 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18824551 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling complexes of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Dec 10;486(2):107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.085. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20816922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of an A-kinase anchoring protein-like suggests an alternative way of PKA anchoring in Plasmodium falciparum.Malar J. 2016 Apr 29;15:248. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1275-9. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 27129434 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase A Opposes the Phosphorylation-dependent Recruitment of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β to A-kinase Anchoring Protein 220.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 7;290(32):19445-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.654822. Epub 2015 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26088133 Free PMC article.
-
Networking with AKAPs: context-dependent regulation of anchored enzymes.Mol Interv. 2010 Apr;10(2):86-97. doi: 10.1124/mi.10.2.6. Mol Interv. 2010. PMID: 20368369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angelo R. and Rubin,C.S. (1998) Molecular characterization of an anchor protein (AKAPCE) that binds the RI subunit (RCE) of type I protein kinase A from Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 14633–14643. - PubMed
-
- Angelo R.G. and Rubin,C.S. (2000) Characterization of structural features that mediate the tethering of Caenorhabditis elegans protein kinase A to a novel A kinase anchor protein. Insights into the anchoring of PKAI isoforms. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 4351–4362. - PubMed
-
- Banky P., Huang,L.J. and Taylor,S.S. (1998) Dimerization/docking domain of the type Iα regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Requirements for dimerization and docking are distinct but overlapping J. Biol. Chem., 273, 35048–35055. - PubMed
-
- Bax A. and Davis,D.G. (1985) MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson., 65, 355–360.
-
- Brunger A.T. (1992) X-PLOR. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

