Molecular basis of thermosensing: a two-component signal transduction thermometer in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 11285232
- PMCID: PMC145467
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1681
Molecular basis of thermosensing: a two-component signal transduction thermometer in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
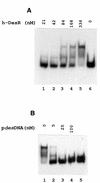
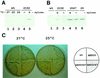
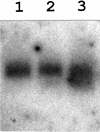
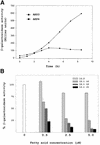
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes respond to a decrease in temperature with the expression of a specific subset of proteins. Although a large body of information concerning cold shock-induced genes has been gathered, studies on temperature regulation have not clearly identified the key regulatory factor(s) responsible for thermosensing and signal transduction at low temperatures. Here we identified a two-component signal transduction system composed of a sensor kinase, DesK, and a response regulator, DesR, responsible for cold induction of the des gene coding for the Delta5-lipid desaturase from Bacillus subtilis. We found that DesR binds to a DNA sequence extending from position -28 to -77 relative to the start site of the temperature-regulated des gene. We show further that unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs), the products of the Delta5-desaturase, act as negative signalling molecules of des transcription. Thus, a regulatory loop composed of the DesK-DesR two-component signal transduction system and UFAs provides a novel mechanism for the control of gene expression at low temperatures.
Figures



References
-
- Choi J.Y., Stukey,J., Hwang,S.Y. and Martin,C.E. (1996) Regulatory elements that control transcription activation and unsaturated fatty acid-mediated repression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae OLE1 gene J. Biol. Chem., 271, 3581–3589. - PubMed
-
- Cronan J.E. Jr and Rock,C.O. (1996) Biosynthesis of membrane lipids. In Neidhart,F.C. et al. (eds), Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2nd edn, Vol. 1. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 612–636.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

