A role for histone deacetylase HDAC1 in modulating the transcriptional activity of MyoD: inhibition of the myogenic program
- PMID: 11285237
- PMCID: PMC145490
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1739
A role for histone deacetylase HDAC1 in modulating the transcriptional activity of MyoD: inhibition of the myogenic program
Abstract
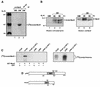
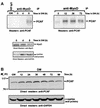
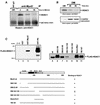
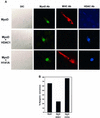
The molecular mechanism(s) that are responsible for suppressing MyoD's transcriptional activities in undifferentiated skeletal muscle cells have not yet been determined. We now show that MyoD associates with a histone deacetylase-1 (HDAC1) in these cells and that this interaction is responsible for silencing MyoD-dependent transcription of endogenous p21 as well as muscle-specific genes. Specifically, we present evidence that HDAC1 can bind directly to MyoD and use an acetylated MyoD as a substrate in vitro, whereas a mutant version of HDAC1 (H141A) can not. Further more, this mutant also fails to repress MyoD-mediated transcription in vivo, and unlike wild-type HDAC1 it can not inhibit myogenic conversion, as judged by confocal microscopy. Finally, we show that an endogenous MyoD can be acetylated upon its conversion to a hypophosphorylated state and only when the cells have been induced to differentiate. These results provide for a model which postulates that MyoD may be co-dependent on HDAC1 and P/CAF for temporally controlling its transcriptional activity before and after the differentiation of muscle cells.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold H.-H. and Winter,B. (1998) Muscle differentiation: more complexity to the network of myogenic regulators. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 539–544. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R., Davis,R.L., Lockshon,D., Turner,D.L. and Weintraub,H. (1990) The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix–loop–helix DNA binding proteins. Cell, 61, 49–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

