Analyses of single-amino-acid substitution mutants of adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K protein
- PMID: 11287579
- PMCID: PMC114175
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4297-4307.2001
Analyses of single-amino-acid substitution mutants of adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K protein
Abstract
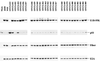
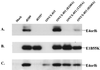
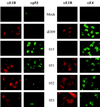
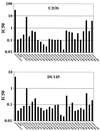
The E1B-55K protein plays an important role during human adenovirus type 5 productive infection. In the early phase of the viral infection, E1B-55K binds to and inactivates the tumor suppressor protein p53, allowing efficient replication of the virus. During the late phase of infection, E1B-55K is required for efficient nucleocytoplasmic transport and translation of late viral mRNAs, as well as for host cell shutoff. In an effort to separate the p53 binding and inactivation function and the late functions of the E1B-55K protein, we have generated 26 single-amino-acid mutations in the E1B-55K protein. These mutants were characterized for their ability to modulate the p53 level, interact with the E4orf6 protein, mediate viral late-gene expression, and support virus replication in human cancer cells. Of the 26 mutants, 24 can mediate p53 degradation as efficiently as the wild-type protein. Two mutants, R240A (ONYX-051) and H260A (ONYX-053), failed to degrade p53 in the infected cells. In vitro binding assays indicated that R240A and H260A bound p53 poorly compared to the wild-type protein. When interaction with another viral protein, E4orf6, was examined, H260A significantly lost its ability to bind E4orf6, while R240A was fully functional in this interaction. Another mutant, T255A, lost the ability to bind E4orf6, but unexpectedly, viral late-gene expression was not affected. This raised the possibility that the interaction between E1B-55K and E4orf6 was not required for efficient viral mRNA transport. Both R240A and H260A have retained, at least partially, the late functions of wild-type E1B-55K, as determined by the expression of viral late proteins, host cell shutoff, and lack of a cold-sensitive phenotype. Virus expressing R240A (ONYX-051) replicated very efficiently in human cancer cells, while virus expressing H260A (ONYX-053) was attenuated compared to wild-type virus dl309 but was more active than ONYX-015. The ability to separate the p53-inactivation activity and the late functions of E1B-55K raises the possibility of generating adenovirus variants that retain the tumor selectivity of ONYX-015 but can replicate more efficiently than ONYX-015 in a broad spectrum of cell types.
Figures




Similar articles
-
E1B-55-kilodalton protein is not required to block p53-induced transcription during adenovirus infection.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7685-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7685-7697.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220443 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus ubiquitin-protein ligase stimulates viral late mRNA nuclear export.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(2):575-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01725-06. Epub 2006 Nov 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17079297 Free PMC article.
-
The large E1B protein together with the E4orf6 protein target p53 for active degradation in adenovirus infected cells.Oncogene. 1998 Jan 22;16(3):349-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201540. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9467960
-
Interactions between adenovirus proteins and the p53 pathway: the development of ONYX-015.Semin Cancer Biol. 2000 Dec;10(6):453-9. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2000.0336. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000. PMID: 11170867 Review.
-
The biology of the adenovirus E1B 55K protein.FEBS Lett. 2019 Dec;593(24):3504-3517. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13694. Epub 2019 Dec 8. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31769868 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mre11 complex is required for ATM activation and the G2/M checkpoint.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 15;22(24):6610-20. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg630. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14657032 Free PMC article.
-
E1B-55-kilodalton protein is not required to block p53-induced transcription during adenovirus infection.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7685-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7685-7697.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220443 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mutations in the adenoviral E1B 55-kilodalton protein coding sequence on viral late mRNA metabolism.J Virol. 2002 May;76(9):4507-19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.9.4507-4519.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11932416 Free PMC article.
-
Role of E1B55K in E4orf6/E1B55K E3 ligase complexes formed by different human adenovirus serotypes.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6232-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00384-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536656 Free PMC article.
-
Ixovex-1, a novel oncolytic E1B-mutated adenovirus.Cancer Gene Ther. 2022 Nov;29(11):1628-1635. doi: 10.1038/s41417-022-00480-3. Epub 2022 May 20. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 35596069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker D D, Berk A J. Adenovirus proteins from both E1B reading frames are required for transformation of rodent cells by viral infection and DNA transfection. Virology. 1987;156:107–121. - PubMed
-
- Beltz G A, Flint S J. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis during adenovirus infection. Restriction of cellular messenger RNA sequences to the nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1979;131:353–373. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff J R, Kirn D H, Williams A, Heise C, Horn S, Muna M, Ng L, Nye J A, Sampson-Johannes A, Fattaey A, McCormick F. An adenovirus mutant that replicates selectively in p53-deficient human tumor cells. Science. 1996;274:373–376. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

