Functional characterization of the N termini of murine leukemia virus envelope proteins
- PMID: 11287584
- PMCID: PMC114180
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4357-4366.2001
Functional characterization of the N termini of murine leukemia virus envelope proteins
Abstract
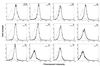
The function of the N terminus of the murine leukemia virus (MuLV) surface (SU) protein was examined. A series of five chimeric envelope proteins (Env) were generated in which the N terminus of amphotropic 4070A was replaced by equivalent sequences from ecotropic Moloney MuLV (M-MuLV). Viral titers of these chimeras indicate that exchange with homologous sequences could be tolerated, up to V17eco/T15ampho (crossover III). Constructs encoding the first 28 amino acids (aa) of ecotropic M-MuLV resulted in Env expression and binding to the receptor; however, the virus titer was reduced 5- to 45-fold, indicating a postbinding block. Additional exchange beyond the first 28 aa of ecotropic MuLV Env resulted in defective protein expression. These N-terminal chimeras were also introduced into the AE4 chimeric Env backbone containing the amphotropic receptor binding domain joined at the hinge region to the ecotropic SU C terminus. In this backbone, introduction of the first 17 aa of the ecotropic Env protein significantly increased the titer compared to that of its parental chimera AE4, implying a functional coordination between the N terminus of SU and the C terminus of the SU and/or transmembrane proteins. These data functionally dissect the N-terminal sequence of the MuLV Env protein and identify differential effects on receptor-mediated entry.
Figures

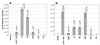

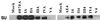
Similar articles
-
Functional interaction between the N- and C-terminal domains of murine leukemia virus surface envelope protein.Virology. 2003 May 25;310(1):130-40. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00111-9. Virology. 2003. PMID: 12788637
-
Second-site changes affect viability of amphotropic/ecotropic chimeric enveloped murine leukemia viruses.J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(2):899-913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.2.899-913.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10623753 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of conformational and cold-sensitive mutations in the MuLV envelope protein.Virology. 2003 Aug 1;312(2):337-49. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00244-7. Virology. 2003. PMID: 12919739
-
Basis for receptor specificity of nonecotropic murine leukemia virus surface glycoprotein gp70SU.J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4632-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.8.4632-4638.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1321266 Free PMC article.
-
A proline-rich motif downstream of the receptor binding domain modulates conformation and fusogenicity of murine retroviral envelopes.J Virol. 1998 Dec;72(12):9955-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.12.9955-9965.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9811733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
G541R within the 4070A TM protein regulates fusion in murine leukemia viruses.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(22):12011-21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12011-12021.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14581538 Free PMC article.
-
G100R mutation within 4070A murine leukemia virus Env increases virus receptor binding, kinetics of entry, and viral transduction efficiency.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):739-43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.739-743.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477879 Free PMC article.
-
Envelope determinants for dual-receptor specificity in feline leukemia virus subgroup A and T variants.J Virol. 2006 Feb;80(4):1619-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.4.1619-1628.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16439518 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion-defective gibbon ape leukemia virus vectors can be rescued by homologous but not heterologous soluble envelope proteins.J Virol. 2002 May;76(9):4267-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.9.4267-4274.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11932392 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic and biological analysis of a laboratory-generated gammaretrovirus xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV).Virus Genes. 2012 Oct;45(2):218-24. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0778-x. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22735937
References
-
- Albritton L M, Tseng L, Scadden D, Cunningham J M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989;57:659–666. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M, Lauring A S, Burns C C, Overbaugh J. Identification of a cellular cofactor required for infection by feline leukemia virus. Science. 2000;287:1828–1830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

