Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter
- PMID: 11287605
- PMCID: PMC86928
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.2991-3000.2001
Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter
Abstract
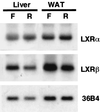
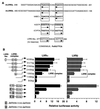
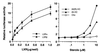
In an attempt to identify transcription factors which activate sterol-regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) transcription, we screened an expression cDNA library from adipose tissue of SREBP-1 knockout mice using a reporter gene containing the 2.6-kb mouse SREBP-1 gene promoter. We cloned and identified the oxysterol receptors liver X receptor (LXRalpha) and LXRbeta as strong activators of the mouse SREBP-1c promoter. In the transfection studies, expression of either LXRalpha or -beta activated the SREBP-1c promoter-luciferase gene in a dose-dependent manner. Deletion and mutation studies, as well as gel mobility shift assays, located an LXR response element complex consisting of two new LXR-binding motifs which showed high similarity to an LXR response element recently found in the ABC1 gene promoter, a reverse cholesterol transporter. Addition of an LXR ligand, 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol, increased the promoter activity. Coexpression of retinoid X receptor (RXR), a heterodimeric partner, and its ligand 9-cis-retinoic acid also synergistically activated the SREBP-1c promoter. In HepG2 cells, SREBP-1c mRNA and precursor protein levels were induced by treatment with 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol and 9-cis-retinoic acid, confirming that endogenous LXR-RXR activation can induce endogenous SREBP-1c expression. The activation of SREBP-1c by LXR is associated with a slight increase in nuclear SREBP-1c, resulting in activation of the gene for fatty acid synthase, one of its downstream genes, as measured by the luciferase assay. These data demonstrate that LXR-RXR can modify the expression of genes for lipogenic enzymes by regulating SREBP-1c expression, providing a novel link between fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta.Genes Dev. 2000 Nov 15;14(22):2819-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.844900. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11090130 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and liver X receptor (LXR) in nutritional regulation of fatty acid metabolism. I. PPARs suppress sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c promoter through inhibition of LXR signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 Jul;17(7):1240-54. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0190. Epub 2003 May 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12730331
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c promoter activity by inhibition of liver X receptor (LXR) binding to LXR response elements.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 18;277(3):1705-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105711200. Epub 2001 Nov 2. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11694526
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein family as global regulators of lipid synthetic genes in energy metabolism.Vitam Horm. 2002;65:167-94. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(02)65064-2. Vitam Horm. 2002. PMID: 12481547 Review.
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 as a dominant transcription factor for gene regulation of lipogenic enzymes in the liver.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2000 Oct;10(7):275-8. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(00)00079-7. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2000. PMID: 11343966 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of liver X receptors (LXRs) genetic variants to gallbladder cancer susceptibility.Tumour Biol. 2013 Dec;34(6):3959-66. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0984-8. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23838803
-
Sensory Neurons, Neuroimmunity, and Pain Modulation by Sex Hormones.Endocrinology. 2021 Aug 1;162(8):bqab109. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab109. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34049389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X receptor α is involved in the transcriptional regulation of the 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase gene.Diabetes. 2012 May;61(5):1062-71. doi: 10.2337/db11-1255. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22415873 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X Receptor β Related to Tumor Progression and Ribosome Gene Expression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020 Sep;35(3):656-668. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.667. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32814418 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of human CYP27 integrates retinoid, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, and liver X receptor signaling in macrophages.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(18):8154-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8154-8166.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15340076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Yoshikawa T, Yahagi N, Hasty A H, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J-I, Harada K, Gotoda T, Sato R, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N. Promoter analysis of the mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP)-1c gene. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:31078–31085. - PubMed
-
- Andersson S, Davis D L, Dahlback H, Jornvall H, Russell D W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:8222–8229. - PubMed
-
- Brown M S, Goldstein J L. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Brown M S, Ye J, Rawson R B, Goldstein J L. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: a control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell. 2000;100:391–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
