Negative regulation of CD4 gene expression by a HES-1-c-Myb complex
- PMID: 11287612
- PMCID: PMC86935
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3071-3082.2001
Negative regulation of CD4 gene expression by a HES-1-c-Myb complex
Abstract
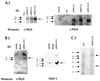
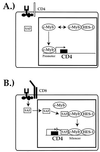
Expression of the CD4 gene is tightly controlled throughout thymopoiesis. The downregulation of CD4 gene expression in CD4(-) CD8(-) and CD4(-) CD8(+) T lymphocytes is controlled by a transcriptional silencer located in the first intron of the CD4 locus. Here, we determine that the c-Myb transcription factor binds to a functional site in the CD4 silencer. As c-Myb is also required for CD4 promoter function, these data indicate that depending on the context, c-Myb plays both positive and negative roles in the control of CD4 gene expression. Interestingly, a second CD4 silencer-binding factor, HES-1, binds to c-Myb in vivo and induces it to become a transcriptional repressor. We propose that the recruitment of HES-1 and c-Myb to the silencer leads to the formation of a multifactor complex that induces silencer function and repression of CD4 gene expression.
Figures







References
-
- Adlam M, Duncan D D, Ng D K, Siu G. Positive selection induces CD4 promoter and enhancer function. Int Immunol. 1997;9:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1995.
-
- Badiani P, Corbella P, Kioussis D, Marvel J, Weston K. Dominant interfering alleles define a role for c-Myb in T-cell development. Genes Dev. 1994;8:770–782. - PubMed
-
- Berg L J, Pullen A M, Fazekas de St. Groth B, Mathis D, Benoist C, Davis M M. Antigen/MHC-specific T cells are preferentially exported from the thymus in the presence of their MHC ligand. Cell. 1989;58:1035–1046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
