Vav-Rac1-mediated activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway plays a major role in stimulation of the distal NFAT site in the interleukin-2 gene promoter
- PMID: 11287617
- PMCID: PMC86940
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3126-3136.2001
Vav-Rac1-mediated activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway plays a major role in stimulation of the distal NFAT site in the interleukin-2 gene promoter
Abstract
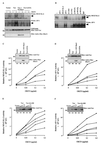
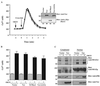
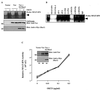
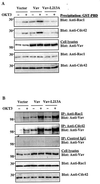
Vav, a hematopoiesis-specific signaling protein, plays an important role in T-cell development and activation. Vav upregulates the expression of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) gene, primarily via activation of the distal NFAT site in the IL-2 gene promoter (NFAT-IL-2). However, since this site cooperatively binds NFAT and AP-1, the relative contribution of Vav to NFAT versus AP-1 activation has not been determined. Here, we studied the respective roles of the AP-1 and NFAT pathways in the T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated, Vav-dependent activation of NFAT-IL-2. Although Vav stimulated the transcriptional activity of an NFAT-IL-2 reporter gene, it failed to stimulate the transcriptional or DNA-binding activities of an AP-1-independent NFAT site derived from the human gamma interferon gene promoter. Vav also did not stimulate detectable Ca(2+) mobilization and nuclear translocation of NFATc or NFATp. On the other hand, Vav induced the activation of Rac1 or Cdc42 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), enhanced the transcriptional and DNA-binding activities of AP-1, and induced increased phosphorylation of c-Jun. Dominant-negative Vav and/or Rac1 mutants blocked the TCR-mediated stimulation of these events, demonstrating the physiological relevance of these effects. Vav also associated with Rac1 or Cdc42 in T cells, and anti-CD3 antibody stimulation enhanced this association. These findings indicate that a Rac1-dependent JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway, rather than the Ca(2+)/NFAT pathway, plays the predominant role in NFAT-IL-2 activation by Vav.
Figures
References
-
- Bagrodia S, Derijard B, Davis R J, Cerione R A. Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27995–27998. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Taylor S J, Creasy C L, Chernoff J, Cerione R A. Identification of a mouse p21Cdc42/Rac activated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22731–22737. - PubMed
-
- Beals C R, Clipstone N A, Ho S N, Crabtree G R. Nuclear localization of NF-ATc by a calcineurin-dependent, cyclosporin-sensitive intramolecular interaction. Genes Dev. 1997;11:824–834. - PubMed
-
- Billadeau D D, Mackie S M, Schoon R A, Leibson P J. Specific subdomains of Vav differentially affect T cell and NK cell activation. J Immunol. 2000;164:3971–3981. - PubMed
-
- Chow C-W, Rincon M, Cavanagh J, Dickens M, Davis R J. Nuclear accumulation of NFAT4 opposed by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1997;278:1638–1641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
