Structure and function of the C-terminal PABC domain of human poly(A)-binding protein
- PMID: 11287632
- PMCID: PMC31848
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.071024998
Structure and function of the C-terminal PABC domain of human poly(A)-binding protein
Abstract
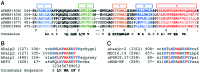
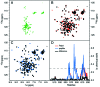
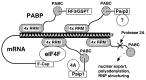
We have determined the solution structure of the C-terminal quarter of human poly(A)-binding protein (hPABP). The protein fragment contains a protein domain, PABC [for poly(A)-binding protein C-terminal domain], which is also found associated with the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. By using peptides derived from PABP interacting protein (Paip) 1, Paip2, and eRF3, we show that PABC functions as a peptide binding domain. We use chemical shift perturbation analysis to identify the peptide binding site in PABC and the major elements involved in peptide recognition. From comparative sequence analysis of PABC-binding peptides, we formulate a preliminary PABC consensus sequence and identify human ataxin-2, the protein responsible for type 2 spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA2), as a potential PABC ligand.
Figures

Comment in
-
Delivering messages from the 3' end.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 10;98(8):4288-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091108098. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11296278 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jacobson A. In: Translational Control. Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, Sonenberg N, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1996. pp. 451–480.
-
- Craig A W, Haghighat A, Yu A T, Sonenberg N. Nature (London) 1998;392:520–523. - PubMed
-
- Khaleghpour K. Ph.D. thesis. Montreal: McGill University; 2000. p. 200.
-
- Hoshino S, Imai M, Kobayashi T, Uchida N, Katada T. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16677–16680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

