Evolution of apparent diffusion coefficient, diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted signal intensity of acute stroke
- PMID: 11290470
- PMCID: PMC7976036
Evolution of apparent diffusion coefficient, diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted signal intensity of acute stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: Serial study of such MR parameters as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), ADC with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (ADC(FLAIR)), and T2-weighted imaging may provide information on the pathophysiological mechanisms of acute ischemic stroke. Our goals were to establish the natural evolution of MR signal intensity characteristics of acute ischemic lesions and to assess the potential of using specific MR parameters to estimate lesion age.
Methods: Five serial echo-planar DWI studies with and without an inversion recovery pulse were performed in 27 patients with acute stroke. The following lesion characteristics were studied: 1) conventional ADC (ADC(CONV)); 2) ADC(FLAIR); 3) DWI signal intensity (SI(DWI)); 4) T2-weighted signal intensity (SI(T2)), and 5) FLAIR signal intensity (SI(FLAIR)).
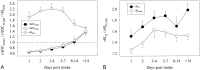
Results: The lesion ADC(CONV) gradually increased from low values during the first week to pseudonormal during the second week to supranormal thereafter. The lesion ADC(FLAIR) showed the same pattern of evolution but with lower absolute values. A low ADC value indicated, with good sensitivity (88%) and specificity (90%), that a lesion was less than 10 days old. All signal intensities remained high throughout follow-up. SI(DWI) showed no significant change during the first week but decreased thereafter. SI(T2) initially increased, decreased slightly during week 2, and again increased after 14 days. SI(FLAIR) showed the same initial increase as the SI(T2) but remained relatively stable thereafter.
Conclusion: Our findings further clarify the time course of stroke evolution on MR parameters and indicate that the ADC map may be useful for estimating lesion age. Application of an inversion recovery pulse results in lower, potentially more accurate, absolute ADC values.
Figures

References
-
- Knight RA, Dereski MO, Helpern JA, Ordidge RJ, Chopp M. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of evolving focal cerebral ischemia: comparison with histopathology in rats. Stroke 1994;25:1252-1261 - PubMed
-
- Pierpaoli C, Righini A, Linfante I, Tao-Cheng JH, Alger JR, Di Chiro G. Histopathologic correlates of abnormal water diffusion in cerebral ischemia: diffusion-weighted MR imaging and light and electron microscopic study. Radiology 1993;189:439-448 - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa Y, Fisher M, Latour LL, Dardzinski BJ, Sotak CH. MRI diffusion mapping of reversible and irreversible ischemic injury in focal brain ischemia. Neurology 1994;44:1484-1490 - PubMed
-
- Welch KM, Windham J, Knight RA, et al. A model to predict the histopathology of human stroke using diffusion and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 1995;26:1983-1989 - PubMed
-
- Barber PA, Darby DG, Desmond PM, et al. Prediction of stroke outcome with echoplanar perfusion- and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neurology 1998;51:418-426 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
