T2 relaxation measurements in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy performed using dual-echo fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging
- PMID: 11290498
- PMCID: PMC7976008
T2 relaxation measurements in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy performed using dual-echo fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine whether dual-echo fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging and corresponding T2 brain maps can show different zones in the affected white matter of patients with cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Ten male patients with cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy underwent imaging performed using dual-echo fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and dual-echo conventional spin-echo MR sequences. Corresponding T2 relaxation maps of the brain were generated. On the basis of dual-echo fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images and T2 maps, the affected white matter could be divided into two distinct zones in four patients with cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.
Figures
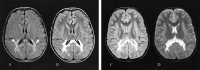
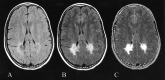
Similar articles
-
Quantitative MR evaluation of intracranial epidermoid tumors by fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging and echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Jun-Jul;22(6):1089-96. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. PMID: 11415903 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: the role of contrast-enhanced MR imaging in predicting disease progression.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 May;21(5):839-44. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. PMID: 10815658 Free PMC article.
-
Fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) magnetic resonance imaging of the brain: a comparison of multi-shot echo-planar and fast spin-echo techniques.Pediatr Radiol. 1997 Jun;27(6):545-9. doi: 10.1007/s002470050177. Pediatr Radiol. 1997. PMID: 9174030
-
Fast spin echo MR imaging.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1999 Aug;9(3):553-76. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1999. PMID: 10433645 Review.
-
MRI surveillance of boys with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy identified by newborn screening: Meta-analysis and consensus guidelines.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 May;44(3):728-739. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12356. Epub 2021 Jan 9. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 33373467 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
3 T MRI relaxometry detects T2 prolongation in the cerebral normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage. 2009 Jul 1;46(3):633-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19281850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS, Suzuki K, Richardson EP Jr. Adrenoleukodystrophy: a clinical and pathological study of 17 cases. Arch Neurol 1975;32:577-591 - PubMed
-
- Powers JM. The pathology of peroxisomal disorders with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1995;54:710-719 - PubMed
-
- Melhem ER, Breiter SN, Ulug AM, Raymond GV, Moser HW. Improved tissue characterization in adrenoleukodystrophy using magnetization transfer imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996;166:689-695 - PubMed
-
- Melhem ER, Whitehead RE, Bert RJ, Caruthers SD. MR imaging of the hippocampus: measurement of T2 with four dual-echo techniques. Radiology 1998;209:551-555 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
