Spinal intradural extramedullary capillary hemangioma: MR imaging findings
- PMID: 11290503
- PMCID: PMC7976030
Spinal intradural extramedullary capillary hemangioma: MR imaging findings
Abstract
Spinal intradural extramedullary capillary hemangiomas are extremely rare. We present the MR imaging and histologic findings in three patients with this abnormality. The three patients were men who had symptoms of either myelopathy (n = 2) or radiculopathy (n = 1). The tumors were well demarcated, 1.5-2.0 cm in diameter, and were located at the posterior or posterolateral portion of the thecal sac (one at the L1 level and the other two at the midthoracic level). On MR images, the tumor showed isointensity relative to the spinal cord on T1-weighted images, hyperintensity on T2-weighted images, and strong homogeneous enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images in all three patients. In two patients, the dural tail sign was observed. Capillary hemangioma should be included in the differential diagnosis of a spinal intradural extramedullary tumor.
Figures
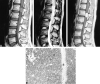


References
-
- Holtzman RNN, Brisson PM, Pearl RE, Gruber ML. Lobular capillary hemangioma of the cauda equina. J Neurosurg 1999;90:239-241 - PubMed
-
- Zander DR, Lander P, Just N, Albrecht S, Mohr G. Magnetic resonance imaging features of a nerve root capillary hemangioma of the spinal cord: case report. Can Assoc Radiol J 1998;49:398-400 - PubMed
-
- Hanakita J, Suwa H, Nagayasu S, Suzuki H. Capillary hemangioma in the cauda equina: neuroradiological findings. Neuroradiology 1991;33:458-461 - PubMed
-
- Mastronardi L, Ferrante L, Scarpinati M, Gagliaridi FM, Celli P, Fortuna A. Intradural extramedullary cavernous angiomas: case report. Neurosurgery 1991;29:924-926 - PubMed
-
- Ueda S, Saito A, Inomori S, Kim I. Cavernous angioma of the cauda equina producing subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 1987;66:134-136 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
