c-MET expression in myofibroblasts: role in autocrine activation and prognostic significance in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 11290563
- PMCID: PMC1891889
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64096-5
c-MET expression in myofibroblasts: role in autocrine activation and prognostic significance in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
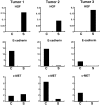
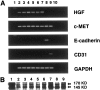
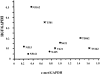
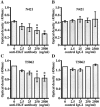
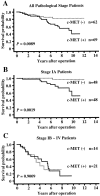
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) plays important roles in tumor development and progression. It is currently thought that the main action of HGF is of a paracrine nature: HGF produced by mesenchymal cells acts on epithelial cells that express its receptor c-MET. In this investigation, we explored the significance of c-MET expression in myofibroblasts, both in culture and in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. We first showed that human myofibroblasts derived from primary lung cancer expressed c-MET mRNA and protein by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis. Proliferation of myofibroblasts was stimulated in a dose-dependent manner by exogenously added recombinant human HGF whereas it was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by neutralizing antibody to HGF. The addition of HGF in the culture medium stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of c-MET. The c-MET protein was immunohistochemically detected in myofibroblasts in the invasive area of lung adenocarcinoma. Finally, the prognostic significance of c-MET expression in stromal myofibroblasts was explored in patients with small-sized lung adenocarcinomas. c-MET-positive myofibroblasts were observed in 69 of 131 cases (53%). A significant relationship between myofibroblast c-MET expression and shortened patient survival was observed in a whole cohort of patients including all pathological stages (two-sided P: = 0.0089 by log-rank test) and in patients with stage IA disease (two-sided P: = 0.0019 by log-rank test). These data suggest that the HGF/c-MET system constitutes an autocrine activation loop in cancer-stromal myofibroblasts. This autocrine system may play a role in invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma.
Figures
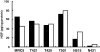



References
-
- Nakamura T: Structure and function of hepatocyte growth factor. Prog Growth Factor Res 1991, 3:67-85 - PubMed
-
- Gak E, Taylor WG, Chan AM, Rubin JS: Processing of hepatocyte growth factor to the heterodimeric form is required for biological activity. FEBS Lett 1992, 311:17-21 - PubMed
-
- Mizuno K, Tanoue Y, Okano I, Harano T, Takada K, Nakamura T: Purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-converting enzyme: activation of pro-HGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994, 198:1161-1169 - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Hiscox S, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, its molecular, cellular and clinical implications in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1999, 29:209-248 - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, Seki T, Shimonishi M, Sugimura A, Tashiro K, Shimizu S: Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 1989, 342:440-443 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

