Flow cytometric determination of cellular sources and frequencies of key cytokine-producing lymphocytes directed against recombinant LACK and soluble Leishmania antigen in human cutaneous leishmaniasis
- PMID: 11292745
- PMCID: PMC98281
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3232-3239.2001
Flow cytometric determination of cellular sources and frequencies of key cytokine-producing lymphocytes directed against recombinant LACK and soluble Leishmania antigen in human cutaneous leishmaniasis
Abstract
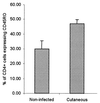
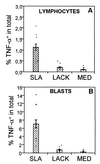
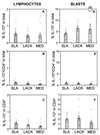
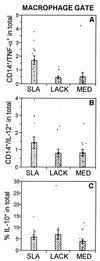
Leishmaniasis, caused by infection with the protozoan parasite Leishmania, affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing serious morbidity and mortality. This study directly determined the frequency of cells producing key immunoregulatory cytokines in response to the recombinant antigen Leishmania homolog of receptors for activated kinase C (LACK) and soluble leishmania antigen (SLA), and it determined relative contributions of these antigens to the overall cytokine profile in individuals infected for the first time with Leishmania braziliensis. All individuals presented with the cutaneous clinical form of leishmaniasis and were analyzed for proliferative responses to LACK antigen and SLA, frequency of lymphocyte subpopulations (analyzed ex vivo), and antigen-induced (LACK and SLA) cytokine production at the single-cell level (determined by flow cytometry). The following were determined. (i) The Th1-type response previously seen in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis is due to gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production by several different sources, listed in order of contribution: CD4(+) T lymphocytes, CD4(-), CD8(-) lymphocytes, and CD8(+) T lymphocytes. (ii) SLA induced a higher frequency of lymphocytes producing IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) than did LACK. (iii) LACK induced an activation of monocyte populations as reflected by an increased percentage of CD14-positive cells. (iv) Neither SLA nor LACK induced detectable frequencies of cells producing interleukin-4 (IL-4) or IL-5. These data demonstrated a multifaceted immune response to SLA in human leishmaniasis involving Th1 CD4(+) T lymphocytes (IFN-gamma(+) and IL-10(-)/IL-4(-)), Tc1 CD8(+) T cells (IFN-gamma(+), and IL-10(-)/IL-4(-)), and a high frequency of TNF-alpha-producing lymphocytes. Moreover, it was determined that the recombinant antigen LACK acts as a weak inducer of Th1-type lymphocyte responses compared to SLA.
Figures


References
-
- Carvalho E M, Bacellar O, Brownell C, Regis T, Coffman R L, Reed S G. Restoration of IFN-gamma production and lymphocyte proliferation in visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1994;152:5949–5956. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho E M, Correia F D, Bacellar O, Almeida R P, Lessa H, Rocha H. Characterization of the immune response in subjects with self-healing cutaneous leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;53:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Coutinho S G, Oliveira M P, Da-Cruz A M, et al. T-cell responsiveness of American cutaneous leishmaniasis patients to purified Leishmania pifanoi amastigote antigens and Leishmania braziliensis promastigote antigens: immunologic patterns associated with cure. Exp Parasitol. 1996;84:144–155. - PubMed
-
- Gazzinelli G, Katz N, Rocha R S, Colley D G. Immune responses during human Schistosomiasis mansoni. VIII. Differential in vitro cellular responsiveness to adult worm and schistosomular tegumental preparations. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983;32:326–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

