Deletion of yeast p24 genes activates the unfolded protein response
- PMID: 11294899
- PMCID: PMC32279
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.957
Deletion of yeast p24 genes activates the unfolded protein response
Abstract
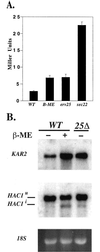
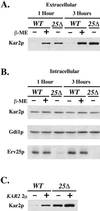
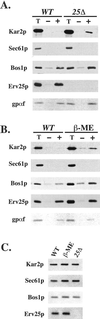
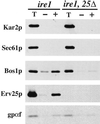
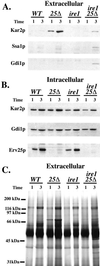
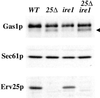
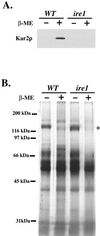
Yeast cells lacking a functional p24 complex accumulate a subset of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and increase the extracellular secretion of HDEL-containing ER residents such as Kar2p/BiP. We report that a loss of p24 function causes activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) and leads to increased KAR2 expression. The HDEL receptor (Erd2p) is functional and traffics in p24 deletion strains as in wild-type strains, however the capacity of the retrieval pathway is exceeded. Other conditions that activate the UPR and elevate KAR2 expression also lead to extracellular secretion of Kar2p. Using an in vitro assay that reconstitutes budding from the ER, we detect elevated levels of Kar2p in ER-derived vesicles from p24 deletion strains and from wild-type strains with an activated UPR. Silencing the UPR by IRE1 deletion diminished Kar2p secretion under these conditions. We suggest that activation of the UPR plays a major role in extracellular secretion of Kar2p.
Figures



References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1997.
-
- Baker D, Hicke L, Rexach M, Schleyer M, Schekman R. Reconstitution of SEC gene product-dependent intercompartmental protein transport. Cell. 1988;54:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, McCaffery JM, Plutner H, Farquhar MG. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is sorted and concentrated during export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;76:841–852. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzsola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

