Roles of phosphatidylethanolamine and of its several biosynthetic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11294902
- PMCID: PMC32282
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.997
Roles of phosphatidylethanolamine and of its several biosynthetic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
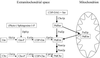
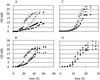
Three different pathways lead to the synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) in yeast, one of which is localized to the inner mitochondrial membrane. To study the contribution of each of these pathways, we constructed a series of deletion mutants in which different combinations of the pathways are blocked. Analysis of their growth phenotypes revealed that a minimal level of PtdEtn is essential for growth. On fermentable carbon sources such as glucose, endogenous ethanolaminephosphate provided by sphingolipid catabolism is sufficient to allow synthesis of the essential amount of PtdEtn through the cytidyldiphosphate (CDP)-ethanolamine pathway. On nonfermentable carbon sources, however, a higher level of PtdEtn is required for growth, and the amounts of PtdEtn produced through the CDP-ethanolamine pathway and by extramitochondrial phosphatidylserine decarboxylase 2 are not sufficient to maintain growth unless the action of the former pathway is enhanced by supplementing the growth medium with ethanolamine. Thus, in the absence of such supplementation, production of PtdEtn by mitochondrial phosphatidylserine decarboxylase 1 becomes essential. In psd1Delta strains or cho1Delta strains (defective in phosphatidylserine synthesis), which contain decreased amounts of PtdEtn, the growth rate on nonfermentable carbon sources correlates with the content of PtdEtn in mitochondria, suggesting that import of PtdEtn into this organelle becomes growth limiting. Although morphological and biochemical analysis revealed no obvious defects of PtdEtn-depleted mitochondria, the mutants exhibited an enhanced formation of respiration-deficient cells. Synthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins is also impaired in PtdEtn-depleted cells, as demonstrated by delayed maturation of Gas1p. Carboxypeptidase Y and invertase, on the other hand, were processed with wild-type kinetics. Thus, PtdEtn depletion does not affect protein secretion in general, suggesting that high levels of nonbilayer-forming lipids such as PtdEtn are not essential for membrane vesicle fusion processes in vivo.
Figures
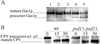

References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996.
-
- Bogdanov M, Umeda M, Dowhan W. Phospholipid-assisted refolding of an integral membrane protein. Minimum structural features for phosphatidylethanolamine to act as a molecular chaperone. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12339–12345. - PubMed
-
- Broekhuyse RM. Phospholipids in tissues of the eye. I. Isolation, characterization and quantitative analysis by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of diacyl and vinyl-ether phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968;152:307–315. - PubMed
-
- Bürgermeister M, Birner R, Hrastnik C, Daum G. Phosphatidylserine decarboxylation and CDP-ethanolamine pathway contribute to the supply of phosphatidylethanolamine to mitochondria of yeast. In: Op den Kamp JAF, editor. NATO-ASI Series: Protein, Lipid and Membrane Traffic. Vol. 322. Amsterdam: IOS Press; 2000. pp. 19–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

