Changes in organization of the endoplasmic reticulum during Xenopus oocyte maturation and activation
- PMID: 11294910
- PMCID: PMC32290
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.1103
Changes in organization of the endoplasmic reticulum during Xenopus oocyte maturation and activation
Abstract
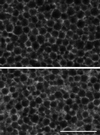
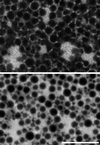
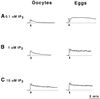
The organization of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the cortex of Xenopus oocytes was investigated during maturation and activation using a green fluorescent protein chimera, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy. Dense clusters of ER developed on the vegetal side (the side opposite the meiotic spindle) during maturation. Small clusters appeared transiently at the time of nuclear envelope breakdown, disappeared at the time of first polar body formation, and then reappeared as larger clusters in mature eggs. The appearance of the large ER clusters was correlated with an increase in releasability of Ca(2+) by IP(3). The clusters dispersed during the Ca(2+) wave at activation. Possible relationships of ER structure and Ca(2+) regulation are discussed.
Figures








References
-
- Campanella C, Andreuccetti P. Ultrastructural observations on cortical endoplasmic reticulum and on residual cortical granules in the egg of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1977;56:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Campanella C, Andreuccetti P, Taddei C, Talevi R. The modifications of cortical endoplasmic reticulum during in vitro maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes and its involvement in cortical granule exocytosis. J Exp Zool. 1984;229:283–293. - PubMed
-
- Carroll DJ, Albay DT, Terasaki M, Jaffe LA, Foltz KR. Identification of PLCgamma-dependent and -independent events during fertilization of sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1999;206:232–247. - PubMed
-
- Carroll J. Na+ – Ca2+ exchange in mouse oocytes: modifications in the regulation of intracellular free Ca2+ during oocyte maturation. J Reprod Fertil. 2000;118:337–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

