Evidence for an intrinsic toxicity of phosphatidylcholine to Sec14p-dependent protein transport from the yeast Golgi complex
- PMID: 11294911
- PMCID: PMC32291
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.1117
Evidence for an intrinsic toxicity of phosphatidylcholine to Sec14p-dependent protein transport from the yeast Golgi complex
Abstract
Yeast phosphatidylinositol-transfer protein (Sec14p) is essential for Golgi secretory function and cell viability. This requirement of Sec14p is relieved by genetic inactivation of the cytidine diphosphate-choline pathway for phosphatidycholine (PtdCho) biosynthesis. Standard phenotypic analyses indicate that inactivation of the phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) pathway for PtdCho biosynthesis, however, does not rescue the growth and secretory defects associated with Sec14p deficiency. We now report inhibition of choline uptake from the media reveals an efficient "bypass Sec14p" phenotype associated with PtdEtn-methylation pathway defects. We further show that the bypass Sec14p phenotype associated with PtdEtn-methylation pathway defects resembles other bypass Sec14p mutations in its dependence on phospholipase D activity. Finally, we find that increased dosage of enzymes that catalyze phospholipase D-independent turnover of PtdCho, via mechanisms that do not result in a direct production of phosphatidic acid or diacylglycerol, effect a partial rescue of sec14-1(ts)-associated growth defects. Taken together, these data support the idea that PtdCho is intrinsically toxic to yeast Golgi secretory function.
Figures








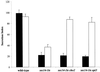




Similar articles
-
Mutations in the CDP-choline pathway for phospholipid biosynthesis bypass the requirement for an essential phospholipid transfer protein.Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):789-800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90508-v. Cell. 1991. PMID: 1997207 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel family of nonclassic yeast phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins whose function modulates phospholipase D activity and Sec14p-independent cell growth.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jun;11(6):1989-2005. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.6.1989. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10848624 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D activity is required for suppression of yeast phosphatidylinositol transfer protein defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 13;95(21):12346-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12346. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9770489 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylcholine synthesis and its catabolism by yeast neuropathy target esterase 1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1771(3):331-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.004. Epub 2006 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 16731034 Review.
-
Surprising roles for phospholipid binding proteins revealed by high throughput genetics.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;88(4):565-74. doi: 10.1139/O09-171. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20651827 Review.
Cited by
-
Localization of lipid raft proteins to the plasma membrane is a major function of the phospholipid transfer protein Sec14.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055388. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383173 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Swiss cheese/neuropathy target esterase activity causes disruption of phosphatidylcholine homeostasis and neuronal and glial death in adult Drosophila.J Neurosci. 2005 Mar 16;25(11):2865-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5097-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15772346 Free PMC article.
-
Translational control of lipogenesis links protein synthesis and phosphoinositide signaling with nuclear division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2022 Jan 4;220(1):iyab171. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab171. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 34849864 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations that affect vacuole biogenesis inhibit proliferation of the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2002 Apr;160(4):1335-52. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.4.1335. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 11973291 Free PMC article.
-
NuA4 Lysine Acetyltransferase Complex Contributes to Phospholipid Homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jun 7;7(6):1799-1809. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.041053. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28455416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonny B, Huber I, Paris S, Chabre M, Cassel D. Activation of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 GTPase-activating protein by phosphatidylcholine-derived diacylglycerols. J Biol Chem, 1997;272:30848–30851. - PubMed
-
- Bankaitis VA, Aitken JR, Cleves AE, Dowhan W. An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature. 1990;347:561–562. - PubMed
-
- Carman GM, Zeimetz GM. Regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13293–13296. - PubMed
-
- Cleves AE, McGee TP, Bankaitis VA. Phospholipid transfer proteins: a biological debut. Trends Cell Biol. 1991a;1:30–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

