Expression of microbial virulence proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae models mammalian infection
- PMID: 11296218
- PMCID: PMC125424
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1840
Expression of microbial virulence proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae models mammalian infection
Abstract
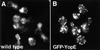
Bacterial virulence proteins that are translocated into eukaryotic cells were expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to model human infection. The subcellular localization patterns of these proteins in yeast paralleled those previously observed during mammalian infection, including localization to the nucleus and plasma membrane. Localization of Salmonella SspA in yeast provided the first evidence that SspA interacts with actin in living cells. In many cases, expression of the bacterial virulence proteins conferred genetically exploitable growth phenotypes. In this way, Yersinia YopE toxicity was demonstrated to be linked to its Rho GTPase activating protein activity. YopE blocked polarization of the yeast cytoskeleton and cell cycle progression, while SspA altered polarity and inhibited depolymerization of the actin cytoskeleton. These activities are consistent with previously proposed or demonstrated effects on higher eukaryotes and provide new insights into the roles of these proteins in pathogenesis: SspA in directing formation of membrane ruffles and YopE in arresting cell division. Thus, study of bacterial virulence proteins in yeast is a powerful system to determine functions of these proteins, probe eukaryotic cellular processes and model mammalian infection.
Figures






References
-
- Ayscough K.R., Stryker,J., Pokala,N., Sanders,M., Crews,P. and Drubin,D.G. (1997) High rates of actin filament turnover in budding yeast and roles for actin in establishment and maintenance of cell polarity revealed using the actin inhibitor latrunculin-A. J. Cell Biol., 137, 399–416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black D.S. and Bliska,J.B. (2000) The RhoGAP activity of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis cytotoxin YopE is required for antiphagocytic function and virulence. Mol. Microbiol., 37, 515–527. - PubMed
-
- Bourdet-Sicard R., Egile,C., Sansonetti,P.J. and Tran Van Nhieu,G. (2000) Diversion of cytoskeletal processes by Shigella during invasion of epithelial cells. Microbes Infect., 2, 813–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

