Mitochondria-to-nucleus stress signaling induces phenotypic changes, tumor progression and cell invasion
- PMID: 11296224
- PMCID: PMC125420
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1910
Mitochondria-to-nucleus stress signaling induces phenotypic changes, tumor progression and cell invasion
Abstract
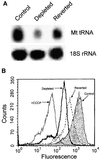
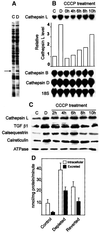
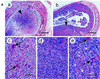
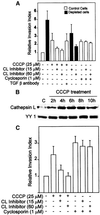
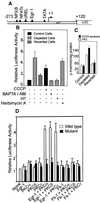
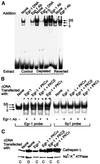
Recently we showed that partial depletion of mitochondrial DNA (genetic stress) or treatment with mitochondrial-specific inhibitors (metabolic stress) induced a stress signaling that was associated with increased cytoplasmic-free Ca(2+) [Ca(2+)](c). In the present study we show that the mitochondria-to-nucleus stress signaling induces invasive phenotypes in otherwise non-invasive C2C12 myoblasts and human pulmonary carcinoma A549 cells. Tumor-specific markers cathepsin L and transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) are overexpressed in cells subjected to mitochondrial genetic as well as metabolic stress. C2C12 myoblasts subjected to stress showed 4- to 6-fold higher invasion through reconstituted Matrigel membrane as well as rat tracheal xenotransplants in Scid mice. Activation of Ca(2+)-dependent protein kinase C (PKC) under both genetic and metabolic stress conditions was associated with increased cathepsin L gene expression, which contributes to increased invasive property of cells. Reverted cells with approximately 70% of control cell mtDNA exhibited marker mRNA contents, cell morphology and invasive property closer to control cells. These results provide insights into a new pathway by which mitochondrial DNA and membrane damage can contribute to tumor progression and metastasis.
Figures

References
-
- Allen J.A. and Coombs,M.M. (1980) Covalent binding of polycyclic aromatic compounds to mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. Nature, 287, 244–245. - PubMed
-
- Atkins K.B. and Troen,B.R. (1995) Phorbol ester stimulated cathepsin L expression in U937 cells. Cell Growth Differ., 6, 713–718. - PubMed
-
- Backer J.M. and Weinstein,I.B. (1980) Mitochondrial DNA is a major cellular target for a dihydrodiol-epoxide derivative of benzo[a]pyrene. Science, 209, 297–299. - PubMed
-
- Biswas G., Adebanjo,O.A., Freedman,B.D., Anandatheerthavarada, H.K., Vijayasarathy,C., Zaidi,M., Kotlikoff,M. and Avadhani,N.G. (1999) Retrograde Ca2+ signaling in C2C12 skeletal myocytes in response to mitochondrial genetic and metabolic stress: a novel mode of inter-organelle crosstalk. EMBO J., 18, 522–533. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

