MOT1-catalyzed TBP-DNA disruption: uncoupling DNA conformational change and role of upstream DNA
- PMID: 11296235
- PMCID: PMC125425
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.2028
MOT1-catalyzed TBP-DNA disruption: uncoupling DNA conformational change and role of upstream DNA
Abstract
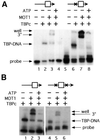
SNF2/SWI2-related ATPases employ ATP hydrolysis to disrupt protein-DNA interactions, but how ATP hydrolysis is coupled to disruption is not understood. Here we examine the mechanism of action of MOT1, a yeast SNF2/SWI2-related ATPase that uses ATP hydrolysis to remove TATA binding protein (TBP) from DNA. MOT1 function requires a 17 bp DNA 'handle' upstream of the TATA box, which must be double stranded. Remarkably, MOT1-catalyzed disruption of TBP-DNA does not appear to require DNA strand separation, DNA bending or twisting of the DNA helix. Thus, TBP-DNA disruption is accomplished in a reaction apparently not driven by a change in DNA structure. MOT1 action is supported by DNA templates in which the handle is connected to the TATA box via single-stranded DNA, indicating that the upstream duplex DNA can be conformationally uncoupled from the TATA box. Combining these results with proposed similarities between SNF2/SWI2 ATPases and helicases, we suggest that MOT1 uses ATP hydrolysis to translocate along the handle and thereby disrupt interactions between TBP and DNA.
Figures








References
-
- Adamkewicz J.I., Mueller,C.G.F., Hansen,K.E., Prud’homme,W.A. and Thorner,J. (2000) Purification and enzymic properties of Mot1 ATPase, a regulator of basal transcription in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 21158–21168. - PubMed
-
- Auble D.T. and Hahn,S. (1993) An ATP-dependent inhibitor of TBP binding to DNA. Genes Dev., 7, 844–856. - PubMed
-
- Auble D.T., Hansen,K.E., Mueller,C.G.F., Lane,W.S., Thorner,J. and Hahn,S. (1994) Mot1, a global repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription, inhibits TBP binding to DNA by an ATP-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev., 8, 1920–1934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

