Visualizing the solvent-inaccessible core of a group II intron ribozyme
- PMID: 11296237
- PMCID: PMC125427
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.2051
Visualizing the solvent-inaccessible core of a group II intron ribozyme
Abstract
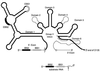
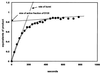
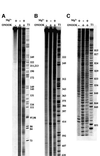
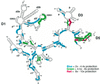
Group II introns are well recognized for their remarkable catalytic capabilities, but little is known about their three-dimensional structures. In order to obtain a global view of an active enzyme, hydroxyl radical cleavage was used to define the solvent accessibility along the backbone of a ribozyme derived from group II intron ai5gamma. These studies show that a highly homogeneous ribozyme population folds into a catalytically compact structure with an extensively internalized catalytic core. In parallel, a model of the intron core was built based on known tertiary contacts. Although constructed independently of the footprinting data, the model implicates the same elements for involvement in the catalytic core of the intron.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Productive folding to the native state by a group II intron ribozyme.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jan 18;315(3):297-310. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5233. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11786013
-
Domains 2 and 3 interact to form critical elements of the group II intron active site.J Mol Biol. 2003 Jul 4;330(2):197-209. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00594-1. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12823961
-
The solvent-protected core of the hairpin ribozyme-substrate complex.Biochemistry. 1998 Oct 20;37(42):14672-82. doi: 10.1021/bi981083n. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9778342
-
Group II introns: structure and catalytic versatility of large natural ribozymes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;38(3):249-303. doi: 10.1080/713609236. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12870716 Review.
-
RNA folds: insights from recent crystal structures.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1999;28:57-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.28.1.57. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1999. PMID: 10410795 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in the Lactococcus lactis Ll.LtrB group II intron that retain mobility in vivo.BMC Mol Biol. 2002 Dec 20;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-3-17. Epub 2002 Dec 20. BMC Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12495443 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic detection of tertiary structural modules in large RNAs and RNP interfaces by Tb-seq.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 9;14(1):3426. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38623-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37296103 Free PMC article.
-
Structural specificity conferred by a group I RNA peripheral element.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jul 19;102(29):10176-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501498102. Epub 2005 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16009943 Free PMC article.
-
RNA catalysis as a probe for chaperone activity of DEAD-box helicases.Methods Enzymol. 2012;511:111-30. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396546-2.00005-X. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22713317 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of a group II intron in the 23S rRNA of a stable ribosome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 27;103(26):9838-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603956103. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16785426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramovitz D.L., Friedman,R.A. and Pyle,A.M. (1996) Catalytic role of 2′-hydroxyl groups within a group II intron active site. Science, 271, 1410–1413. - PubMed
-
- Ban N., Nissen,P., Hansen,J., Moore,P.B. and Steitz,T.A. (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science, 289, 905–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

