Toward rules for 1:1 polyamide:DNA recognition
- PMID: 11296283
- PMCID: PMC31837
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.081070798
Toward rules for 1:1 polyamide:DNA recognition
Abstract
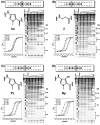
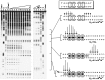
Polyamides composed of four amino acids, imidazole (Im), pyrrole (Py), hydroxypyrrole (Hp), and beta-alanine (beta), are synthetic ligands that form highly stable complexes in the minor groove of DNA. Although specific pairing rules within the 2:1 motif can be used to distinguish the four Watson. Crick base pairs, a comparable recognition code for 1:1 polyamide:DNA complexes had not been described. To set a quantitative baseline for the field, the sequence specificities of Im, Py, Hp, and beta for the four Watson. Crick base pairs were determined for two polyamides, Im-beta-ImPy-beta-Im-beta-ImPy-beta-Dp (1, for Im, Py, and beta) and Im-beta-ImHp-beta-Im-beta-ImPy-beta-Dp (2, for Hp), in a 1:1 complex within the DNA sequence context 5'-AAAGAGAAGAG-3'. Im residues do not distinguish G,C from A,T but bind all four base pairs with high affinity. Py and beta residues exhibit > or = 10-fold preference for A,T over G,C base pairs. The Hp residue displays a unique preference for a single A.T base pair with an energetic penalty.
Figures


References
-
- Dervan P B, Bürli R W. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1999;3:688–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

