Spatial and temporal emergence of high proliferative potential hematopoietic precursors during murine embryogenesis
- PMID: 11296291
- PMCID: PMC31868
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.071002398
Spatial and temporal emergence of high proliferative potential hematopoietic precursors during murine embryogenesis
Abstract
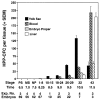
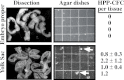
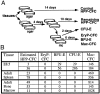
During mouse embryogenesis, two waves of hematopoietic progenitors originate in the yolk sac. The first wave consists of primitive erythroid progenitors that arise at embryonic day 7.0 (E7.0), whereas the second wave consists of definitive erythroid progenitors that arise at E8.25. To determine whether these unilineage hematopoietic progenitors arise from multipotential precursors, we investigated the kinetics of high proliferative potential colony-forming cells (HPP-CFC), multipotent precursors that give rise to macroscopic colonies when cultured in vitro. No HPP-CFC were found at presomite stages (E6.5-E7.5). Rather, HPP-CFC were detected first at early somite stages (E8.25), exclusively in the yolk sac. HPP-CFC were found subsequently in the bloodstream at higher levels than the remainder of the embryo proper. However, the yolk sac remains the predominant site of HPP-CFC expansion (>100-fold) until the liver begins to serve as the major hematopoietic organ at E11.5. On secondary replating, embryonic HPP-CFC give rise to definitive erythroid and macrophage (but not primitive erythroid) progenitors. Our findings support the hypothesis that definitive but not primitive hematopoietic progenitors originate from yolk sac-derived HPP-CFC during late gastrulation.
Figures


References
-
- Osawa M, Hanada K, Hamada H, Nakauchi H. Science. 1996;273:242–245. - PubMed
-
- Moore M A S. Blood. 1991;78:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Bertoncello I. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;177:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Bradley T R, Hodgson G S. Blood. 1979;54:1446–1450. - PubMed
-
- McNiece I K, Williams N T, Johnson G R, Kriegler A B, Bradley T R, Hodgson G S. Exp Hematol (Charlottesville, Va) 1987;15:972–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

