Diethylstilbestrol regulates trophoblast stem cell differentiation as a ligand of orphan nuclear receptor ERR beta
- PMID: 11297507
- PMCID: PMC312665
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.873401
Diethylstilbestrol regulates trophoblast stem cell differentiation as a ligand of orphan nuclear receptor ERR beta
Abstract
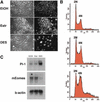
The orphan nuclear receptor ERR beta is expressed in undifferentiated trophoblast stem cell lines and extraembryonic ectoderm, and genetic ablation of ERR beta results in abnormal trophoblast proliferation and precocious differentiation toward the giant cell lineage. Here, we show that the synthetic estrogen diethylstilbestrol (DES) promotes coactivator release from ERR beta and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Strikingly, treatment of trophoblast stem cells with DES led to their differentiation toward the polyploid giant cell lineage. In addition, DES-treated pregnant mice exhibited abnormal early placenta development associated with an overabundance of trophoblast giant cells and an absence of diploid trophoblast. These results define a novel pathway for DES action and provide evidence for steroidlike control of trophoblast development.
Figures


References
-
- Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Jones YZ, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR, Koder A, Evans RM. PPARγ is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:585–595. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg B, Evans RM. Orphan nuclear receptors: New ligands and new possibilities. Genes & Dev. 1998;12:3149–3155. - PubMed
-
- Ciruna BG, Rossant J. Expression of the T-box gene Eomesodermin during early mouse development. Mech Dev. 1999;81:199–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
