Transforming growth factor-beta - and tumor necrosis factor-alpha -mediated induction and proteolytic activation of MMP-9 in human skin
- PMID: 11297541
- PMCID: PMC2651823
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M010839200
Transforming growth factor-beta - and tumor necrosis factor-alpha -mediated induction and proteolytic activation of MMP-9 in human skin
Abstract
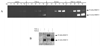
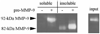
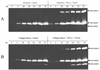
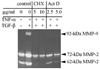
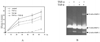
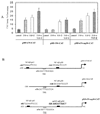
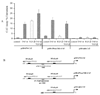
Both cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are active during physiologic and pathologic processes such as cancer metastasis and wound repair. We have systematically studied cytokine-mediated MMP regulation. Cytokine-mediated proteinase induction and activation were initially investigated in organ-cultured human skin followed by determination of underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms using isolated skin cells. In this report we demonstrate that tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) synergistically induce pro-MMP-9 in human skin as well as isolated dermal fibroblasts and epidermal keratinocytes. Furthermore, TNF-alpha promotes proteolytic activation of pro-MMP-9 by conversion of the 92-kDa pro-MMP-9 to the 82-kDa active enzyme. This activation occurred only in skin organ culture and not by either isolated fibroblasts or keratinocyte, although the pro-MMP-9 activation could be measured in a cell-free system derived from TNF-alpha-activated skin. The cytokine-mediated induction of pro-MMP-9 in dermal fibroblasts was evident by increased mRNA. At the transcription level, we examined the cytokine-mediated transactivation of the 5'-region promoter of the human MMP-9 in dermal fibroblasts. The results demonstrated that TNF-alpha and TGF-beta could independently stimulate the 5'-flanking 670-base pair promoter. A TGF-beta-response element (-474) and an NF-kappaB-binding site (-601) were identified to be the cis-elements for TGF-beta or TNF-alpha activation, respectively. Taken together, these findings suggest a specific mechanism whereby multiple cytokines can regulate MMP-9 expression/activation in the cells of human skin. These results imply roles for these cytokines in the regulation of MMP-9 in physiologic and pathologic tissue remodeling.
Figures



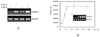
References
-
- Leibovich SJ, Polverini PJ, Shepard HM, Wiseman DM, Shively V, Nuseir N. Nature. 1987;329:630–632. - PubMed
-
- Garner WL, Karmiol S, Rodriguez JL, Smith DJ, Jr, Phan SH. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1993;101:875–879. - PubMed
-
- Cooney R, Iocono J, Maish G, Smith JS, Ehrlich P. J. Trauma. 1997;42:415–420. - PubMed
-
- Kitzis V, Engrav LH, Quinn LS. J. Surg. Res. 1999;87:134–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

