The role of IFN-gamma in systemic lupus erythematosus: a challenge to the Th1/Th2 paradigm in autoimmunity
- PMID: 11299053
- PMCID: PMC128889
- DOI: 10.1186/ar290
The role of IFN-gamma in systemic lupus erythematosus: a challenge to the Th1/Th2 paradigm in autoimmunity
Abstract
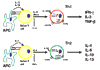
The classification of T helper cells into type 1 (Th1) and type 2 (Th2) led to the hypothesis that Th1 cells and their cytokines (interleukin [IL]-2, interferon [IFN]-gamma) are involved in cell-mediated autoimmune diseases, and that Th2 cells and their cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13) are involved in autoantibody(humoral)-mediated autoimmune diseases. However, this paradigm has been refuted by recent studies in several induced and spontaneous mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus, which showed that IFN-gamma is a major effector molecule in this disease. These and additional findings, reviewed here, suggest that these two cross-talking classes of cytokines can exert autoimmune disease-promoting or disease-inhibiting effects without predictability or strict adherence to the Th1-versus-Th2 dualism.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bone MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Mosmann TR. Differentiation of effector phenotypes of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Fundamental Immunology. 1998. pp. 879–908.
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- O'Garra A. Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity. 1998;8:275–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical