Association of spectrin-like proteins with the actin-organized aggregate of endoplasmic reticulum in the Spitzenkörper of gravitropically tip-growing plant cells
- PMID: 11299343
- PMCID: PMC88819
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.125.4.1611
Association of spectrin-like proteins with the actin-organized aggregate of endoplasmic reticulum in the Spitzenkörper of gravitropically tip-growing plant cells
Abstract
Spectrin-like epitopes were immunochemically detected and immunofluorescently localized in gravitropically tip-growing rhizoids and protonemata of characean algae. Antiserum against spectrin from chicken erythrocytes showed cross-reactivity with rhizoid proteins at molecular masses of about 170 and 195 kD. Confocal microscopy revealed a distinct spherical labeling of spectrin-like proteins in the apices of both cell types tightly associated with an apical actin array and a specific subdomain of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the ER aggregate. The presence of spectrin-like epitopes, the ER aggregate, and the actin cytoskeleton are strictly correlated with active tip growth. Application of cytochalasin D and A23187 has shown that interfering with actin or with the calcium gradient, which cause the disintegration of the ER aggregate and abolish tip growth, inhibits labeling of spectrin-like proteins. At the beginning of the graviresponse in rhizoids the labeling of spectrin-like proteins remained in its symmetrical position at the cell tip, but was clearly displaced to the upper flank in gravistimulated protonemata. These findings support the hypothesis that a displacement of the Spitzenkörper is required for the negative gravitropic response in protonemata, but not for the positive gravitropic response in rhizoids. It is evident that the actin/spectrin system plays a role in maintaining the organization of the ER aggregate and represents an essential part in the mechanism of gravitropic tip growth.
Figures


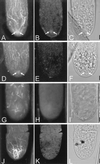

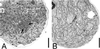

References
-
- Bartnik E, Hejnowicz Z, Sievers A. Shuttle-like movements of Golgi vesicles in the tip of growing Chara rhizoids. Protoplasma. 1990;159:1–8.
-
- Bartnik E, Sievers A. In vivo observation of a spherical aggregate of endoplasmic reticulum and of Golgi vesicles in the tip of fast-growing Chara rhizoids. Planta. 1988;176:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Baumann O. Association of spectrin with a subcompartment of the endoplasmic reticulum in honeybee photoreceptor cells. Cell Motil Cytoskel. 1998;41:74–86. - PubMed
-
- Beck KA, Buchanan JA, Nelson WJ. Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195-kDa ankyrin isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1239–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

