A novel dark-inducible protein, LeDI-2, and its involvement in root-specific secondary metabolism in Lithospermum erythrorhizon
- PMID: 11299363
- PMCID: PMC88839
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.125.4.1831
A novel dark-inducible protein, LeDI-2, and its involvement in root-specific secondary metabolism in Lithospermum erythrorhizon
Abstract
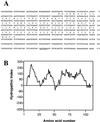
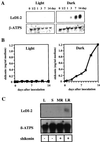
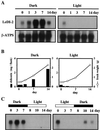
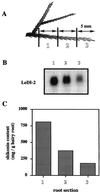
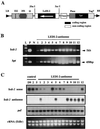
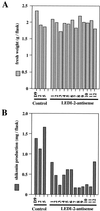
Lithospermum erythrorhizon produces red naphthoquinone pigments that are shikonin derivatives. They are accumulated exclusively in the roots of this plant. The biosynthesis of shikonin is strongly inhibited by light, even though other environmental conditions are optimized. Thus, L. erythrorhizon dark-inducible genes (LeDIs) were isolated to investigate the regulatory mechanism of shikonin biosynthesis. LeDI-2, showing the strict dark-specific expression, was further characterized by use of cell suspension cultures and hairy root cultures as model systems. Its mRNA accumulation showed a similar pattern with that of shikonin. In the intact plants LeDI-2 expression was observed solely in the root, and the longitudinal distribution of its mRNA was also in accordance to that of shikonin. LeDI-2 encoded a very hydrophobic polypeptide of 114 amino acids that shared significant similarities with some root-specific polypeptides such as ZRP3 (maize) and RcC3 (rice). Reduction of LeDI-2 expression by its antisense DNA in hairy roots of L. erythrorhizon decreased the shikonin accumulation, whereas other biosynthetic enzymes, e.g. p-hydroxybenzoic acid:geranyltransferase, which catalyzed a critical biosynthetic step, showed similar activity as the wild-type clone. This is the first report of the gene that is involved in production of secondary metabolites without affecting biosynthetic enzyme activities.
Figures


References
-
- Aleith F, Richter G. Gene expression during induction of somatic embryogenesis in carrot cell suspensions. Planta. 1990;183:17–24. - PubMed
-
- Cashmore AR, Jarillo JA, Wu YJ, Liu D. Cryptochromes: blue light receptors for plant and animals. Science. 1999;284:760–765. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW, Song JY, Kwon YM, Kim SG. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a proline-rich 14-kDa protein in developing cortical cells of the roots of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) seedling. Plant Mol Biol. 1996;30:973–982. - PubMed
-
- Coupe SA, Taylor JE, Isaac PG, Roberts JA. Identification and characterization of a proline-rich mRNA that accumulates during pod development in oil seed rape (Brassica napus L.) Plant Mol Biol. 1993;23:1223–1232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

