Cell migration: GAPs between membrane traffic and the cytoskeleton
- PMID: 11306546
- PMCID: PMC1083869
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve072
Cell migration: GAPs between membrane traffic and the cytoskeleton
Abstract
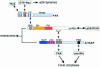
During cell migration, coordination between membrane traffic, cell substrate adhesion and actin reorganization is required for protrusive activity to occur at the leading edge. Actin organization is regulated by Rho family GTPases and, with a contribution from the endocytic cycle, serves to extend the cell front. The details of the molecular mechanisms that direct membrane traffic at sites of adhesion and rearrange actin at the cell edge are still unknown. However, recent findings show that a number of multi-domain proteins characterized by an ArfGAP domain interact with both actin-regulating and integrin-binding proteins, as well as affecting Rac-mediated protrusive activity and cell migration. Some of these proteins have been shown to localize to endocytic compartments and to have a role in regulating endocytosis. Given the participation of Arf proteins in regulating membrane traffic, one appealing hypothesis is that the ArfGAPs act as molecular devices that coordinate membrane traffic and cytoskeletal reorganization during cell motility.
Figures

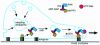

Similar articles
-
p95-APP1 links membrane transport to Rac-mediated reorganization of actin.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;2(8):521-30. doi: 10.1038/35019561. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10934473
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating the subcellular localization of p95-APP1 between the endosomal recycling compartment and sites of actin organization at the cell surface.J Cell Sci. 2001 Dec;114(Pt 24):4509-20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.24.4509. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11792816
-
Role of actin polymerization and adhesion to extracellular matrix in Rac- and Rho-induced cytoskeletal reorganization.J Cell Biol. 1997 Aug 25;138(4):913-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.4.913. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9265656 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization.Cancer Sci. 2005 Jul;96(7):379-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00062.x. Cancer Sci. 2005. PMID: 16053508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. Mol Biol Cell. 1992. PMID: 1611153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arf6 plays an early role in platelet activation by collagen and convulxin.Blood. 2006 Apr 15;107(8):3145-52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-3563. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16352809 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis and spatial restriction of cell signaling.Mol Oncol. 2009 Aug;3(4):280-96. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2009.05.008. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Mol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19570732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crk associates with a multimolecular Paxillin/GIT2/beta-PIX complex and promotes Rac-dependent relocalization of Paxillin to focal contacts.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jul;14(7):2818-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0497. Epub 2003 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12857867 Free PMC article.
-
Rab-mediated vesicular transport is required for neuronal positioning in the developing Drosophila visual system.Mol Brain. 2010 Jun 11;3:19. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-3-19. Mol Brain. 2010. PMID: 20540751 Free PMC article.
-
PKC epsilon controls the traffic of beta1 integrins in motile cells.EMBO J. 2002 Jul 15;21(14):3608-19. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf371. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12110574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagrodia S., Taylor, S.J., Jordan, K.A., Van Aelst, L. and Cerione, R.A. (1998) A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 23633–23636. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S., Bailey, D., Lenard, Z., Hart, M., Guan, J.L., Premont, R.T., Taylor, S.J. and Cerione, R.A. (1999) A tyrosine-phosphorylated protein that binds to an important regulatory region on the cool family of p21-activated kinase-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 22393–22400. - PubMed
-
- Borisy G.G. and Svitkina, T.M. (2000) Actin machinery: pushing the envelope. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12, 104–112. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher M.S. (1996) Getting membrane flow and the cytoskeleton to cooperate in moving cells. Cell, 87, 601–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

