Intrathecal HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 induces enhanced pain states mediated by spinal cord proinflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 11306633
- PMCID: PMC6762530
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-08-02808.2001
Intrathecal HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 induces enhanced pain states mediated by spinal cord proinflammatory cytokines
Abstract
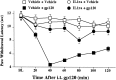
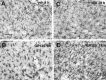
Perispinal (intrathecal) injection of the human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein gp120 creates exaggerated pain states. Decreases in response thresholds to both heat stimuli (thermal hyperalgesia) and light tactile stimuli (mechanical allodynia) are rapidly induced after gp120 administration. gp120 is the portion of HIV-1 that binds to and activates microglia and astrocytes. These glial cells have been proposed to be key mediators of gp120-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia because these pain changes are blocked by drugs thought to affect glial function preferentially. The aim of the present series of studies was to determine whether gp120-induced pain changes involve proinflammatory cytokines [interleukin-1beta (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)], substances released from activated glia. IL-1 and TNF antagonists each prevented gp120-induced pain changes. Intrathecal gp120 produced time-dependent, site-specific increases in TNF and IL-1 protein release into lumbosacral CSF; parallel cytokine increases in lumbar dorsal spinal cord were also observed. Intrathecal administration of fluorocitrate (a glial metabolic inhibitor), TNF antagonist, and IL-1 antagonist each blocked gp120-induced increases in spinal IL-1 protein. These results support the concept that activated glia in dorsal spinal cord can create exaggerated pain states via the release of proinflammatory cytokines.
Figures










References
-
- Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Piccioli P, Costa A, Florio T, Schettini G. Glial and neuronal cells express functional chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its natural ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1. J Neurochem. 1999;73:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Ballestas ME, Benveniste EN. Interleukin-1-beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated regulation of ICAM-1 gene expression in astrocytes requires protein kinase C activity. Glia. 1995;14:267–278. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN. Cytokine expression in the nervous system. In: Keane RW, Hickey WF, editors. Immunology of the nervous system. Oxford UP; New York: 1997. pp. 419–459.
-
- Bhat NR, Zhang P, Bhat AN. Cytokine induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase in an oligodendrocyte cell line: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Neurochem. 1999;72:472–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
