Differential modulation of endothelin ligand-induced contraction in isolated tracheae from endothelin B (ET(B)) receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 11309263
- PMCID: PMC1572715
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703957
Differential modulation of endothelin ligand-induced contraction in isolated tracheae from endothelin B (ET(B)) receptor knockout mice
Abstract
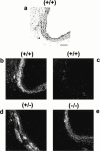
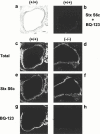
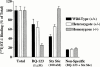
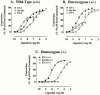
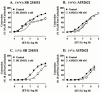
The role of endothelin B (ET(B)) receptors in mediating ET ligand-induced contractions in mouse trachea was examined in ET(B) receptor knockout animals. Autoradiographic binding studies, using [(125)I]-ET-1, confirmed the presence of ET(A) receptors in tracheal and bronchial airway smooth muscle from wild-type (+/+) and homozygous recessive (-/-) ET(B) receptor knockout mice. In contrast, ET(B) receptors were not detected in airway tissues from (-/-) mice. In tracheae from (+/+) mice, the rank order of potencies of the ET ligands was sarafotoxin (Stx) S6c>ET-1>ET-3; Stx S6c had a lower efficacy than ET-1 or ET-3. In tissues from (-/-) mice there was no response to Stx S6c (up to 0.1 microM), whereas the maximum responses and potencies of ET-1 and ET-3 were similar to those in (+/+) tracheae. ET-3 concentration-response curve was biphasic in (+/+) tissues (via ET(A) and ET(B) receptor activation), and monophasic in (-/-) preparations (via stimulation of only ET(A) receptors). In (+/+) preparations SB 234551 (1 nM), an ET(A) receptor-selective antagonist, inhibited the secondary phase, but not the first phase, of the ET-3 concentration-response curve, whereas A192621 (100 nM), an ET(B) receptor-selective antagonist, had the opposite effect. In (-/-) tissues SB 234551 (1 nM), but not A192621 (100 nM), produced a rightward shift in ET-3 concentration-response curves. The results confirm the significant influence of both ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in mediating ET-1-induced contractions in mouse trachea. Furthermore, the data do not support the hypothesis of atypical ET(B) receptors. In this preparation ET-3 is not an ET(B) receptor-selective ligand, producing contractions via activation of both ET(A) and ET(B) receptors.
Figures

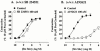
Similar articles
-
Endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced contraction in rat isolated trachea: involvement of ETA and ETB receptors and multiple signal transduction systems.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):435-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13829.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8220905 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation by endothelin-1 of cholinergic nerve-mediated contractions in mouse trachea via activation of ETB receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(3):563-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb17176.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7735683 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of endothelin B (ETB) receptors in rabbit isolated pulmonary artery and bronchus.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;118(5):1209-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15525.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8818345 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin receptors in gastrointestinal smooth muscle.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005 Dec;6(6):547-57. doi: 10.2174/138920305774933295. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005. PMID: 16381603 Review.
-
Enrasentan, an antagonist of endothelin receptors.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Spring;21(1):1-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00102.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 12595914 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro measurements of tracheal constriction using mice.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 25;(64):3703. doi: 10.3791/3703. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22760068 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and progesterone regulate expression of the endothelins in the rhesus macaque endometrium.Hum Reprod. 2011 Jul;26(7):1715-28. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der115. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Hum Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21505040 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling and regulation of G protein-coupled receptors in airway smooth muscle.Respir Res. 2003;4(1):2. Epub 2003 Mar 14. Respir Res. 2003. PMID: 12648290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ARAI H., NAKAO K., TAKAYA K., HOSADA K., OGAWA Y., NAKANISHI S., IMURA H. The human endothelin-B receptor gene: structural organization and chromosomal assignment. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:3463–3470. - PubMed
-
- BAX W.A., SAXENA P.R. The current endothelin receptor classification: time for reconsideration. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994;15:379–386. - PubMed
-
- BERTHIAUME N., YANAGISAWA M., LABONTÉ J., D'ORLÉANS-JUSTE P. Heterozygous knockout-out of ETB receptors induces BQ-123-sensitive hypertension in the mouse. Hypertension. 2000;36:1002–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

