Myopalladin, a novel 145-kilodalton sarcomeric protein with multiple roles in Z-disc and I-band protein assemblies
- PMID: 11309420
- PMCID: PMC2169455
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.2.413
Myopalladin, a novel 145-kilodalton sarcomeric protein with multiple roles in Z-disc and I-band protein assemblies
Abstract
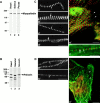
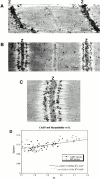
We describe here a novel sarcomeric 145-kD protein, myopalladin, which tethers together the COOH-terminal Src homology 3 domains of nebulin and nebulette with the EF hand motifs of alpha-actinin in vertebrate Z-lines. Myopalladin's nebulin/nebulette and alpha-actinin-binding sites are contained in two distinct regions within its COOH-terminal 90-kD domain. Both sites are highly homologous with those found in palladin, a protein described recently required for actin cytoskeletal assembly (Parast, M.M., and C.A. Otey. 2000. J. Cell Biol. 150:643-656). This suggests that palladin and myopalladin may have conserved roles in stress fiber and Z-line assembly. The NH(2)-terminal region of myopalladin specifically binds to the cardiac ankyrin repeat protein (CARP), a nuclear protein involved in control of muscle gene expression. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy studies revealed that myopalladin also colocalized with CARP in the central I-band of striated muscle sarcomeres. Overexpression of myopalladin's NH(2)-terminal CARP-binding region in live cardiac myocytes resulted in severe disruption of all sarcomeric components studied, suggesting that the myopalladin-CARP complex in the central I-band may have an important regulatory role in maintaining sarcomeric integrity. Our data also suggest that myopalladin may link regulatory mechanisms involved in Z-line structure (via alpha-actinin and nebulin/nebulette) to those involved in muscle gene expression (via CARP).
Figures




References
-
- Arber S., Hunter J.J., Ross J., Jr., Hongo M., Sansig G., Borg J., Perriard J.C., Chien K.R., Caroni P. MLP-deficient mice exhibit a disruption of cardiac cytoarchitectural organization, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Cell. 1997;88:393–403. - PubMed
-
- Beggs A.H., Byers T.J., Knoll J.H., Boyce F.M., Bruns G.A., Kunkel L.M. Cloning and characterization of two human skeletal muscle alpha-actinin genes located on chromosomes 1 and 11. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:9281–9288. - PubMed
-
- Centner T., Fougerousse F., Freiburg A., Witt C., Beckmann J.S., Granzier H., Trombitas K., Gregorio C.C., Labeit S. Molecular tools for the study of titin's differential expression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000;481:35–49. - PubMed
-
- Chu W., Burns D.K., Swerlick R.A., Presky D.H. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine-inducible nuclear protein from human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:10236–10245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

