Interleukin-10 prevents glutamate-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by blocking caspase-3-like activity
- PMID: 11312295
- PMCID: PMC6762554
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-03104.2001
Interleukin-10 prevents glutamate-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by blocking caspase-3-like activity
Abstract
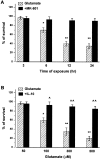
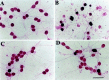
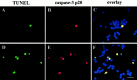
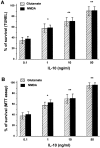
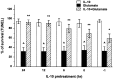
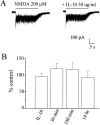
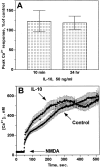
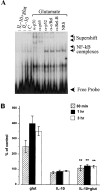
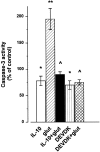
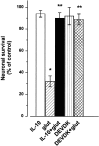
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) has been shown to reduce neuronal degeneration after CNS injury. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective properties of this cytokine are still under investigation. Glutamate exacerbates secondary injury caused by trauma. Thus, we examined whether IL-10 prevents glutamate-mediated cell death. We used rat cerebellar granule cells in culture because these neurons undergo apoptosis upon exposure to toxic concentrations of glutamate (100-500 microm) or NMDA (300 microm). Pretreatment of cerebellar granule cells with IL-10 (1-50 ng/ml) elicited a dose- and time-dependent reduction of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Most importantly, IL-10 reduced the number of apoptotic cells when added to the cultures together or 1 hr after glutamate. Using patch-clamping and fluorescence Ca(2+) imaging techniques, we examined whether IL-10 prevents glutamate toxicity by blocking the function of NMDA channel. IL-10 failed to affect NMDA channel properties and to reduce NMDA-mediated rise in intracellular Ca(2+). Thus, this cytokine appears to prevent glutamate toxicity by a mechanism unrelated to a blockade of NMDA receptor function. Various proteases, such as caspase-3, and transcription factors, such as nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), have been proposed to participate in glutamate-mediated apoptosis. Thus, we examined whether IL-10 modulates the activity of these apoptotic markers. IL-10 blocked both the glutamate-mediated induction of caspase-3 as well as NF-kappaB DNA binding activity, suggesting that the neuroprotective properties of IL-10 may rely on its ability to block the activity of proapoptotic proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Anegawa NJ, Lynch DR, Verdoorn TA, Pritchett DB. Transfection of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in a nonneuronal cell line leads to cell death. J Neurochem. 1995;64:2004–2012. - PubMed
-
- Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron. 1995;15:961–973. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Berkman N, John M, Roesems G, Jose PJ, Barnes PJ, Chung KF. Inhibition of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 α expression by IL-10. J Immunol. 1995;155:4412–4418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
