3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)-induced learning and memory impairments depend on the age of exposure during early development
- PMID: 11312307
- PMCID: PMC6762552
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-03228.2001
3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)-induced learning and memory impairments depend on the age of exposure during early development
Abstract
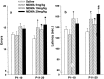
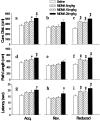
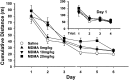
Use of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; ecstasy) has increased dramatically in recent years, yet little is known about its effects on the developing brain. Neonatal rats were administered MDMA on days 1-10 or 11-20 (analogous to early and late human third trimester brain development). MDMA exposure had no effect on survival but did affect body weight gain during treatment. After treatment, body weight largely recovered to 90-95% of controls. MDMA exposure on days 11-20 resulted in dose-related impairments of sequential learning and spatial learning and memory, whereas neonatal rats exposed on days 1-10 showed almost no effects. At neither stage of exposure did MDMA-treated offspring show effects on swimming ability or cued learning. Brain region-specific dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine changes were small and were not correlated to learning changes. These findings suggest that MDMA may pose a previously unrecognized risk to the developing brain by inducing long-term deleterious effects on learning and memory.
Figures



References
-
- Aguirre N, Barrionuevo M, Lasheras B, Del Rio J. The role of dopaminergic systems in the perinatal sensitivity to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;286:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Allen RP, McCann UD, Ricaurte GA. Persistent effects of (+/−)3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “Ecstasy”) on human sleep. Sleep. 1993;16:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Good MA, Butcher SP, Ramsay M, Morris RGM. Distinct components of spatial learning revealed by prior training and NMDA receptor blockade. Nature. 1995;378:182–186. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Yeh SY, O'Hearn E, Molliver ME, Kuhar MJ, DeSouza EB. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and 3,4-methlenedioxyamphetamine destroy serotonin terminals in rat brain: quantification of neurodegeneration by measurement of [3H]paroxetine-labeled serotonin uptake sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;242:911–916. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Sharkey J, Kuhar MJ, De Souza EB. Neuroanatomic specificity and time course of alterations in rat brain serotonergic pathways induced by MDMA (3,4-methylenedoxymethamphetamine): assessment using quantitative autoradiograph. Synapse. 1991;8:249–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
