Apoptosis mediates decrease in cellularity during the regression of Arthus reaction in cornea
- PMID: 11316727
- PMCID: PMC1723963
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.85.5.613
Apoptosis mediates decrease in cellularity during the regression of Arthus reaction in cornea
Abstract
Background/aims: The Arthus type allergic reaction is characterised by inflammatory cell infiltration and marked neovascularisation in the cornea. During the healing stages, inflammatory cells and newly formed microvessels gradually disappear. The aim was to establish whether apoptosis affected the regression of inflammatory cells and newly formed microvessels, in order to define more clearly the cellular mechanisms involved in the pathobiology of corneal diseases.
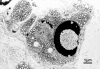
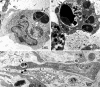
Methods: Albino male rabbits were injected subcutaneously with 5 mg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA) incorporated in Freund's complete adjuvant twice weekly. Under the anaesthesia, 30 microl of a 0.5 mg/ml BSA solution was injected into the central corneal stroma to induce an Arthus type allergic reaction. The injured corneas were collected at various time points ranging from 3 to 20 days. Apoptotic cells were identified by both light microscopy using in situ TdT-dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) method and electron microscopy.
Results: With increasing time after induction of the Arthus reaction, marked neovascularisation and infiltrated inflammatory cells such as polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) and plasma cells were observed in the cornea. Thereafter, the inflammatory cells and newly formed microvessels gradually disappeared. Coincidently, the numbers of microvessel endothelial cells and infiltrated inflammatory cells undergoing apoptosis were increased. Apoptotic bodies were taken up by macrophages, PMNs, as well as myofibroblasts derived presumably from transformation of migrated keratocytes.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that regression of the cellular infiltrates and microvessel endothelial cells associated with the Arthus reaction in the cornea occurs via apoptosis. This finding adds insights into the cellular mechanisms regulating the pathobiology of corneal diseases.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
