Detection of acute bee paralysis virus and black queen cell virus from honeybees by reverse transcriptase pcr
- PMID: 11319129
- PMCID: PMC92884
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.5.2384-2387.2001
Detection of acute bee paralysis virus and black queen cell virus from honeybees by reverse transcriptase pcr
Abstract
A reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) assay was developed for the detection of acute bee paralysis virus (ABPV) and black queen cell virus (BQCV), two honeybee viruses. Complete genome sequences were used to design unique PCR primers within a 1-kb region from the 3' end of both genomes to amplify a fragment of 900 bp from ABPV and 700 bp from BQCV. The combined guanidinium thiocyanate and silica membrane method was used to extract total RNA from samples of healthy and laboratory-infected bee pupae. In a blind test, RT-PCR successfully identified the samples containing ABPV and BQCV. Sensitivities were approximately 1,600 genome equivalents of purified ABPV and 130 genome equivalents of BQCV.
Figures
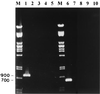


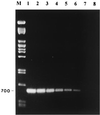
References
-
- Allen M, Ball B. The incidence and world distribution of the honey bee viruses. Bee World. 1996;77:141–162.
-
- Allen M F, Ball B V, White R F, Antoniw J F. The detection of acute paralysis virus in Varroa jacobsoni by the use of a simple indirect ELISA. J Apic Res. 1986;25:100–105.
-
- Anderson D L. Pathogens and queen bees. Australasian Beekeeper. 1993;94:292–296.
-
- Bailey L, Ball B V, Perry J N. Association of viruses with two protozoal pathogens of the honey bee. Ann Appl Biol. 1983;103:13–20.
-
- Bailey L, Gibbs A J, Woods R D. Two viruses from adult honey bees (Apis mellifera Linnaeus) Virology. 1963;21:390–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

