Mapping of contact sites in complex formation between light-activated rhodopsin and transducin by covalent crosslinking: use of a chemically preactivated reagent
- PMID: 11320238
- PMCID: PMC33132
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051632998
Mapping of contact sites in complex formation between light-activated rhodopsin and transducin by covalent crosslinking: use of a chemically preactivated reagent
Abstract
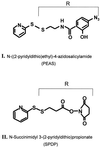
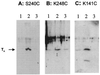
Contact sites in interaction between light-activated rhodopsin and transducin (T) have been investigated by using a chemically preactivated crosslinking reagent, N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate. The 3 propionyl-N-succinimidyl group in the reagent was attached by a disulfide exchange reaction to rhodopsin mutants containing single reactive cysteine groups in the cytoplasmic loops. Complex formation between the derivatized rhodopsin mutants and T was carried out by illumination at lambda > 495 nm. Subsequent increase in pH (from 6 to 7.5 or higher) of the complex resulted in crosslinking of rhodopsin to the T(alpha) subunit. Crosslinking to T(alpha) was demonstrated for the rhodopsin mutants K141C, S240C, and K248C, and the crosslinked sites in T(alpha) were identified for the rhodopsin mutant S240C. The peptides carrying the crosslinking moiety were isolated from the trypsin-digested peptide mixture, and their identification was carried out by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. The main site of crosslinking is within the peptide sequence, Leu-19-Arg-28 at the N-terminal region of T(alpha). The total results show that both the N and the C termini of T(alpha) are in close vicinity to the third cytoplasmic loop of rhodopsin in the complex between rhodopsin and T.
Figures





Comment in
-
How activated receptors couple to G proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):4819-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011099798. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11320227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

