Glimepiride block of cloned beta-cell, cardiac and smooth muscle K(ATP) channels
- PMID: 11325810
- PMCID: PMC1572773
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704062
Glimepiride block of cloned beta-cell, cardiac and smooth muscle K(ATP) channels
Abstract
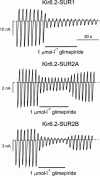
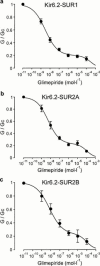
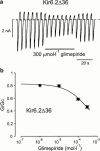
1. We examined the effect of the sulphonylurea glimepiride on three types of recombinant ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels. 2. K(ATP) channels share a common pore-forming subunit, Kir6.2, which associates with different sulphonylurea receptor isoforms (SUR1 in beta-cells, SUR2A in heart and SUR2B in smooth muscle). 3. Kir6.2 was coexpressed with SUR1, SUR2A or SUR2B in Xenopus oocytes and macroscopic K(ATP) currents were recorded from giant inside-out membrane patches. Glimepiride was added to the intracellular membrane surface. 4. Glimepiride inhibited Kir6.2/SUR currents by interaction with two sites: a low-affinity site on Kir6.2 (IC(50)= approximately 400 microM) and a high-affinity site on SUR (IC(50)=3.0 nM for SUR1, 5.4 nM for SUR2A and 7.3 nM for SUR2B). The potency of glimepiride at the high-affinity site is close to that observed for glibenclamide (4 nM for SUR1, 27 nM for SUR2A), which has a similar structure. 5. Glimepiride inhibition of Kir6.2/SUR2A and Kir6.2/SUR2B currents, but not Kir6.2/SUR1 currents, reversed rapidly. 6. Our results indicate that glimepiride is a high-affinity sulphonylurea that does not select between the beta-cell, cardiac and smooth muscle types of recombinant K(ATP) channel, when measured in inside-out patches. High-affinity inhibition is mediated by interaction of the drug with the sulphonylurea receptor subunit of the channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of mitiglinide (S 21403) on Kir6.2/SUR1, Kir6.2/SUR2A and Kir6.2/SUR2B types of ATP-sensitive potassium channel.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Apr;132(7):1542-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703962. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11264248 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of metabolic inhibition on glimepiride block of native and cloned cardiac sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;136(5):746-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704770. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12086984 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of repaglinide on cloned beta cell, cardiac and smooth muscle types of ATP-sensitive potassium channels.Diabetologia. 2001 Jun;44(6):747-56. doi: 10.1007/s001250051684. Diabetologia. 2001. PMID: 11440368
-
Sulfonylurea sensitivity of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels from beta cells and extrapancreatic tissues.Metabolism. 2000 Oct;49(10 Suppl 2):3-6. Metabolism. 2000. PMID: 11078468 Review.
-
Differential selectivity of insulin secretagogues: mechanisms, clinical implications, and drug interactions.J Diabetes Complications. 2003 Mar-Apr;17(2 Suppl):11-5. doi: 10.1016/s1056-8727(02)00272-6. J Diabetes Complications. 2003. PMID: 12623163 Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfonylureas in the Current Practice of Type 2 Diabetes Management: Are They All the Same? Consensus from the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries Advisory Board on Sulfonylureas.Diabetes Ther. 2021 Aug;12(8):2115-2132. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01059-1. Epub 2021 May 13. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 33983614 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (efavirenz and nevirapine) on the pharmacodynamic activity of gliclazide in animal models.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2009 Oct 9;1(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-1-15. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2009. PMID: 19825151 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioselectivity of the sulphonylurea HMR 1098: studies on native and recombinant cardiac and pancreatic K(ATP) channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(2):480-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704455. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11815384 Free PMC article.
-
Is impairment of ischaemic preconditioning by sulfonylurea drugs clinically important?Heart. 2004 Jan;90(1):9-12. doi: 10.1136/heart.90.1.9. Heart. 2004. PMID: 14676228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasorelaxant Effects of Syzygium samarangense (Blume) Merr. and L.M.Perry Extract Are Mediated by NO/cGMP Pathway in Isolated Rat Thoracic Aorta.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;15(11):1349. doi: 10.3390/ph15111349. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGUILAR-BRYAN L., NICHOLS C.G., WECHSLER S.W., CLEMENT J.P., BOYD A.E., GONZALEZ G., HERRERA-SOSA H., NGUY K., BRYAN J., NELSON D.A. Cloning of the β-cell high-affinity sulphonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science. 1995;268:423–425. - PubMed
-
- ASHCROFT F.M., ASHCROFT S.J.H. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell. Signal. 1990;2:197–214. - PubMed
-
- ASHCROFT F.M., GRIBBLE F.M. Correlating structure and function in ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:288–294. - PubMed
-
- ASHCROFT F.M., GRIBBLE F.M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels and insulin secretion. Diabetologia. 1999;42:903–919. - PubMed
-
- ASHCROFT F.M., RORSMAN P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog. Biophys. Molec. Biol. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

