Genetic diversity of Neisseria lactamica strains from epidemiologically defined carriers
- PMID: 11325979
- PMCID: PMC88014
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.5.1710-1715.2001
Genetic diversity of Neisseria lactamica strains from epidemiologically defined carriers
Abstract
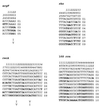
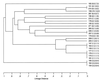
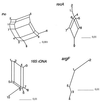
We assessed the genetic diversity of 26 Neisseria lactamica strains from epidemiologically related sources, i.e., groups of kindergartens and primary schools in three Bavarian towns, by the partial sequencing of the argF, rho, recA, and 16S ribosomal genes. We found a total of 17 genotypes, of which 12 were found only in one strain. The genotypes comprised 5 alleles of the argF gene, 9 of rho, 8 of recA, and 10 of the 16S ribosomal DNA. Sequence analysis by determination of homoplasy ratios and split decomposition analysis revealed abundant recombination within N. lactamica.
Figures
References
-
- Bandelt H J, Dress A W. Split decomposition: a new and useful approach to phylogenetic analysis of distance data. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1992;1:242–252. - PubMed
-
- Barrett S J, Sneath P H. A numerical phenotypic taxonomic study of the genus Neisseria. Microbiology. 1994;140:2867–2891. - PubMed
-
- Blakebrough I S, Greenwood B M, Whittle H C, Bradley A K, Gilles H M. The epidemiology of infections due to Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica in a northern Nigerian community. J Infect Dis. 1982;146:626–637. - PubMed
-
- Bowler L D, Zhang Q Y, Riou J Y, Spratt B G. Interspecies recombination between the penA genes of Neisseria meningitidis and commensal Neisseria species during the emergence of penicillin resistance in N. meningitidis: natural events and laboratory simulation. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:333–337. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

