Dynamics of a nosocomial outbreak of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing the PER-1 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase
- PMID: 11326005
- PMCID: PMC88040
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.5.1865-1870.2001
Dynamics of a nosocomial outbreak of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing the PER-1 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase
Abstract
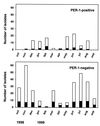
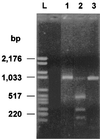
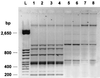
From November 1998 to August 1999, a large outbreak occurred in the general intensive care unit of the Ospedale di Circolo in Varese (Italy), caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing the PER-1 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. A total of 108 clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa resistant to broad-spectrum cephalosporins were recovered from 18 patients. Epidemic isolates were characterized by synergy between clavulanic acid and ceftazidime, cefepime, and aztreonam. Isoelectric focusing of crude bacterial extracts detected two nitrocefin-positive bands with pI values of 8.0 and 5.3. PCR amplification and characterization of the amplicons by restriction analysis and direct sequencing indicated that the epidemic isolates carried a bla(PER-1) determinant. The outbreak was of clonal origin as shown by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis. This technique also indicated that the epidemic strain was not related to three other PER-1-positive isolates obtained at the same hospital in 1997. Typing by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR showed that minor genetic variations occurred during the outbreak. The epidemic strain was characterized by a multiple-drug-resistance phenotype that remained unchanged over the outbreak, including extended-spectrum cephalosporins, monobactams, aminoglycosides, and fluoroquinolones. Isolation of infected patients and appropriate carbapenem therapy were successful in ending the outbreak. Our report indicates that the bla(PER-1) resistance determinant may become an emerging therapeutic problem in Europe.
Figures

References
-
- Arruda E A, Marinho I S, Boulos M, Sinto S I, Caiaffa H H, Mendes C M, Oplustil C P, Sader H, Levy C E, Levin A S. Nosocomial infections caused by multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999;20:620–623. - PubMed
-
- Bonfiglio G, Carciotto V, Russo G, Stefani S, Schito G C, Debbia E, Nicoletti G. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an Italian survey. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998;41:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Bush L M, Johnson C C. Ureidopenicillins and beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000;14:409–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

