Layer-specific intracolumnar and transcolumnar functional connectivity of layer V pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex
- PMID: 11331387
- PMCID: PMC6762473
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-10-03580.2001
Layer-specific intracolumnar and transcolumnar functional connectivity of layer V pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex
Abstract
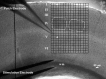
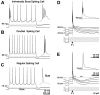
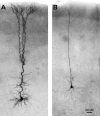
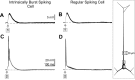
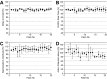
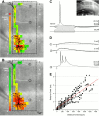
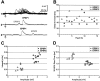
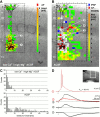
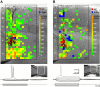
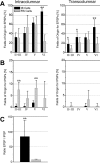
Layer V pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex are considered to play an important role in intracolumnar and transcolumnar signal processing. However, the precise circuitry mediating this processing is still incompletely understood. Here we obtained detailed maps of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs onto the two major layer V pyramidal cell subtypes, intrinsically burst spiking (IB) and regular spiking (RS) cells, using a combination of caged glutamate photolysis, whole-cell patch-clamp recording, and three-dimensional reconstruction of biocytin-labeled cells. To excite presynaptic neurons with laminar specificity, the release of caged glutamate was calibrated and restricted to small areas of 50 x 50 microm in all cortical layers and in at least two neighboring barrel-related columns. IB cells received intracolumnar excitatory input from all layers, with the largest EPSP amplitudes originating from neurons in layers IV and VI. Prominent transcolumnar excitatory inputs were provided by presynaptic neurons also located in layers IV, V, and VI of neighboring columns. Inhibitory inputs were rare. In contrast, RS cells received distinct intracolumnar inhibitory inputs, especially from layers II/III and V. Intracolumnar excitatory inputs to RS cells were prominent from layers II-V, but relatively weak from layer VI. Conspicuous transcolumnar excitatory inputs could be evoked solely in layers IV and V. Our results show that layer V pyramidal cells are synaptically driven by presynaptic neurons located in every layer of the barrel cortex. RS cells seem to be preferentially involved in intracolumnar signal processing, whereas IB cells effectively integrate excitatory inputs across several columns.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A gradual depth-dependent change in connectivity features of supragranular pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex.Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(3):1317-37. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0726-8. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 24569853 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology, electrophysiology and functional input connectivity of pyramidal neurons characterizes a genuine layer va in the primary somatosensory cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2006 Feb;16(2):223-36. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhi100. Epub 2005 May 4. Cereb Cortex. 2006. PMID: 15872153
-
Efficacy and connectivity of intracolumnar pairs of layer 2/3 pyramidal cells in the barrel cortex of juvenile rats.J Physiol. 2006 Sep 1;575(Pt 2):583-602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.105106. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16793907 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping functional connectivity in barrel-related columns reveals layer- and cell type-specific microcircuits.Brain Struct Funct. 2007 Sep;212(2):107-19. doi: 10.1007/s00429-007-0147-z. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2007. PMID: 17717691 Review.
-
Excitatory signal flow and connectivity in a cortical column: focus on barrel cortex.Brain Struct Funct. 2007 Jul;212(1):3-17. doi: 10.1007/s00429-007-0144-2. Epub 2007 Jun 1. Brain Struct Funct. 2007. PMID: 17717695 Review.
Cited by
-
High serotonin levels during brain development alter the structural input-output connectivity of neural networks in the rat somatosensory layer IV.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Jun 7;7:88. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00088. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23761736 Free PMC article.
-
Variation and convergence in the morpho-functional properties of the mammalian neocortex.Front Syst Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;18:1413780. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2024.1413780. eCollection 2024. Front Syst Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38966330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological Characteristics of Electrophysiologically Characterized Layer Vb Pyramidal Cells in Rat Barrel Cortex.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 5;11(10):e0164004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164004. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27706253 Free PMC article.
-
Number and laminar distribution of neurons in a thalamocortical projection column of rat vibrissal cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2010 Oct;20(10):2277-86. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq067. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 20534784 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of synaptic connectivity between layer 1 inhibitory interneurons and layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in the rat neocortex.Cereb Cortex. 2011 Aug;21(8):1818-26. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq257. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Cereb Cortex. 2011. PMID: 21220765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience. 1991;41:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Ahissar E, Sosnik R, Haidarliu S. Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory thalamocortical pathway. Nature. 2000;406:302–306. - PubMed
-
- Amitai Y. Membrane potential oscillations underlying firing patterns in neocortical neurons. Neuroscience. 1994;63:151–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
