Association and spreading of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex from a discrete roX1 chromatin entry site
- PMID: 11331589
- PMCID: PMC125240
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2236
Association and spreading of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex from a discrete roX1 chromatin entry site
Abstract
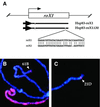
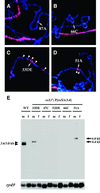
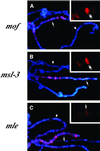
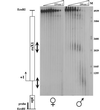
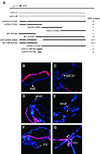
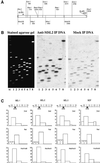
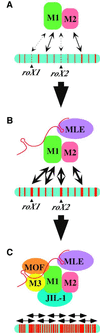
In Drosophila, dosage compensation is controlled by the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex consisting of MSL proteins and roX RNAs. The MSL complex is specifically localized on the male X chromosome to increase its expression approximately 2-fold. We recently proposed a model for the targeted assembly of the MSL complex, in which initial binding occurs at approximately 35 dispersed chromatin entry sites, followed by spreading in cis into flanking regions. Here, we analyze one of the chromatin entry sites, the roX1 gene, to determine which sequences are sufficient to recruit the MSL complex. We found association and spreading of the MSL complex from roX1 transgenes in the absence of detectable roX1 RNA synthesis from the transgene. We mapped the recruitment activity to a 217 bp roX1 fragment that shows male-specific DNase hypersensitivity and can be preferentially cross-linked in vivo to the MSL complex. When inserted on autosomes, this small roX1 segment is sufficient to produce an ectopic chromatin entry site that can nucleate binding and spreading of the MSL complex hundreds of kilobases into neighboring regions.
Figures
References
-
- Akhtar A. and Becker,P.B. (2000) Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell, 5, 367–375. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A., Zink,D. and Becker,P.B. (2000) Chromodomains are protein–RNA interaction modules. Nature, 407, 405–409. - PubMed
-
- Amrein H. and Axel,R. (1997) Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell, 88, 459–469. - PubMed
-
- Bone J.R., Lavender,J., Richman,R., Palmer,M.J., Turner,B.M. and Kuroda,M.I. (1994) Acetylated histone H4 on the male X chromosome is associated with dosage compensation in Drosophila. Genes Dev., 8, 96–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

