Interleukin 3-dependent activation of DREAM is involved in transcriptional silencing of the apoptotic Hrk gene in hematopoietic progenitor cells
- PMID: 11331593
- PMCID: PMC125442
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2286
Interleukin 3-dependent activation of DREAM is involved in transcriptional silencing of the apoptotic Hrk gene in hematopoietic progenitor cells
Abstract
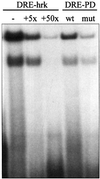
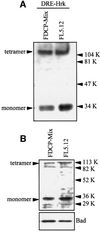
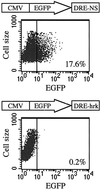
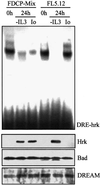
The apoptotic protein Hrk is expressed in hematopoietic progenitors after growth factor deprivation. Here we identify a silencer sequence in the 3' untranslated region of the hrk gene that binds to the transcriptional repressor DREAM in interleukin-3 (IL-3)-dependent hematopoietic progenitor cells, and abrogates the expression of reporter genes when located downstream of the open reading frame. In addition, the binding of DREAM to the hrk gene is reduced or eliminated when cells are cultured in the absence of IL-3 or treated with a calcium ionophore or a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-specific inhibitor, suggesting that both calcium mobilization and phosphorylation can regulate the transcriptional activity of DREAM. Furthermore, we have shown that DREAM is phosphorylated by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent, but Akt-independent pathway. In all cases, loss of the DREAM-DNA binding complex was correlated with increased levels of Hrk and apoptosis. These data suggest that IL-3 may trigger the activation of DREAM through different signaling pathways, which in turn binds to a silencer sequence in the hrk gene and blocks transcription, avoiding inappropriate cell death in hematopoietic progenitors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fas signaling and blockade of Bcr-Abl kinase induce apoptotic Hrk protein via DREAM inhibition in human leukemia cells.Haematologica. 2002 Sep;87(9):903-7. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12217801
-
Lithium activates the Wnt and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Akt signaling pathways to promote cell survival in the absence of soluble survival factors.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Apr;288(4):F703-13. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00189.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15572521
-
Catalytic-dependent and -independent roles of SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase in interleukin-3 signaling.Oncogene. 2003 Sep 4;22(38):5995-6004. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206846. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12955078
-
The DREAM-DRE interaction: key nucleotides and dominant negative mutants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Dec 20;1498(2-3):162-8. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(00)00092-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11108959 Review.
-
Ca2+-dependent transcriptional repression and derepression: DREAM, a direct effector.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2001 Feb;12(1):59-63. doi: 10.1006/scdb.2000.0218. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11162748 Review.
Cited by
-
DREAM mediated regulation of GCM1 in the human placental trophoblast.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e51837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051837. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23300953 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator (DREAM) in rat spinal cord and upregulation of its expression during inflammatory pain.Neurochem Res. 2007 Sep;32(9):1592-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9364-3. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17562172
-
Transcriptional repressor DREAM regulates T-lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine gene expression.EMBO J. 2005 Oct 19;24(20):3555-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600810. Epub 2005 Sep 22. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 16177826 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and Ca2+ links the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 3 to memory and sensory pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Aug;30(1):91-116. doi: 10.1385/MN:30:1:091. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15247490 Review.
-
Cell Death Signaling.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Dec 1;7(12):a006080. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006080. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26626938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bouillet P., Metcalf,D., Huang,D.C., Tarlinton,D.M., Kay,T.W., Kontgen,F., Adams,J.M. and Strasser,A. (1999) Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science, 286, 1735–1738. - PubMed
-
- Caron-Leslie L.A. and Cidlowski,J.A. (1991) Similar actions of glucocorticoids and calcium on the regulation of apoptosis in S49 cells. Mol. Endocrinol., 5, 1169–1179. - PubMed
-
- Carrion A.M., Link,W.A., Ledo,F., Mellstrom,B. and Naranjo,J.R. (1999) DREAM is a calcium-regulated transcriptional repressor. Nature, 398, 80–84. - PubMed
-
- Catlett-Falcone R. et al. (1999) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity, 10, 105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

