RNA binding in an Sm core domain: X-ray structure and functional analysis of an archaeal Sm protein complex
- PMID: 11331594
- PMCID: PMC125243
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2293
RNA binding in an Sm core domain: X-ray structure and functional analysis of an archaeal Sm protein complex
Abstract
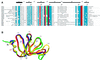
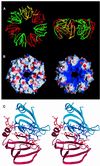
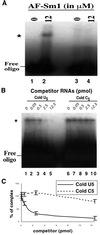
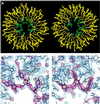
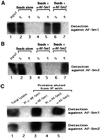
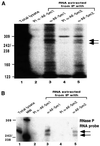
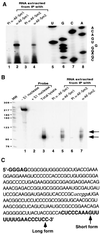
Eukaryotic Sm and Sm-like proteins associate with RNA to form the core domain of ribonucleoprotein particles involved in pre-mRNA splicing and other processes. Recently, putative Sm proteins of unknown function have been identified in Archaea. We show by immunoprecipitation experiments that the two Sm proteins present in Archaeoglobus fulgidus (AF-Sm1 and AF-Sm2) associate with RNase P RNA in vivo, suggesting a role in tRNA processing. The AF-Sm1 protein also interacts specifically with oligouridylate in vitro. We have solved the crystal structures of this protein and a complex with RNA. AF-Sm1 forms a seven-membered ring, with the RNA interacting inside the central cavity on one face of the doughnut-shaped complex. The bases are bound via stacking and specific hydrogen bonding contacts in pockets lined by residues highly conserved in archaeal and eukaryotic Sm proteins, while the phosphates remain solvent accessible. A comparison with the structures of human Sm protein dimers reveals closely related monomer folds and intersubunit contacts, indicating that the architecture of the Sm core domain and RNA binding have been conserved during evolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Archaeal Sm proteins form heptameric and hexameric complexes: crystal structures of the Sm1 and Sm2 proteins from the hyperthermophile Archaeoglobus fulgidus.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jun 28;320(1):129-42. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00406-0. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12079339
-
Crystal structure of a heptameric Sm-like protein complex from archaea: implications for the structure and evolution of snRNPs.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 15;309(4):915-23. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4693. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11399068
-
Crystal structures of the Pyrococcus abyssi Sm core and its complex with RNA. Common features of RNA binding in archaea and eukarya.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 10;278(2):1239-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207685200. Epub 2002 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12409299
-
Archaeal and eukaryotic homologs of Hfq: A structural and evolutionary perspective on Sm function.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):636-51. doi: 10.4161/rna.24538. Epub 2013 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23579284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SMN complex: an assembly machine for RNPs.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:313-20. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.001. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381311 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of Sm genes reveal their involvement in early somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 3;15(4):e0230795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230795. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32243451 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary diversification of the Sm family of RNA-associated proteins.Mol Biol Evol. 2008 Nov;25(11):2255-67. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn175. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Mol Biol Evol. 2008. PMID: 18687770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structural basis of Edc3- and Scd6-mediated activation of the Dcp1:Dcp2 mRNA decapping complex.EMBO J. 2012 Jan 18;31(2):279-90. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.408. Epub 2011 Nov 15. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22085934 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae LSM1 gene that affect mRNA decapping and 3' end protection.Genetics. 2005 May;170(1):33-46. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.034322. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15716506 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and RNA-binding properties of the bacterial LSm protein Hfq.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):610-8. doi: 10.4161/rna.24201. Epub 2013 Mar 27. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23535768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

