SMNrp is an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor required for the formation of the mature spliceosome
- PMID: 11331595
- PMCID: PMC125440
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2304
SMNrp is an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor required for the formation of the mature spliceosome
Abstract
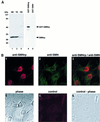
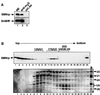
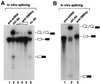
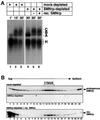
SMNrp, also termed SPF30, has recently been identified in spliceosomes assembled in vitro. We have functionally characterized this protein and show that it is an essential splicing factor. We show that SMNrp is a 17S U2 snRNP-associated protein that appears in the pre-spliceosome (complex A) and the mature spliceosome (complex B) during splicing. Immunodepletion of SMNrp from nuclear extract inhibits the first step of pre-mRNA splicing by preventing the formation of complex B. Re-addition of recombinant SMNrp to immunodepleted extract reconstitutes both spliceosome formation and splicing. Mutations in two domains of SMNrp, although similarly deleterious for splicing, differed in their consequences on U2 snRNP binding, suggesting that SMNrp may also engage in interactions with splicing factors other than the U2 snRNP. In agreement with this, we present evidence for an additional interaction between SMNrp and the [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNP. A candidate that may mediate this interaction, namely the U4/U6-90 kDa protein, has been identified. We suggest that SMNrp, as a U2 snRNP-associated protein, facilitates the recruitment of the [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNP to the pre-spliceosome.
Figures







References
-
- Behrens S.E. and Lührmann,R. (1991) Immunoaffinity purification of a U4/U6⋅U5 tri-snRNP from human cells. Genes Dev., 5, 1439–1452. - PubMed
-
- Behrens S.E., Gallison,F., Legrain,P. and Lührmann,R. (1993a) Evidence that the 60-kDa protein of 17S U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is immunologically and functionally related to the yeast PRP9 splicing factor and is required for the efficient formation of prespliceosome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 8229–8233. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

